Summary of Home-Tech Grow(H.T.G.) Blog Post
- All posts will be displayed here.
- There are more than 150 posts on home technology.
- Click on the text to get the details of the posts for Biomass Energy, smartphone technology, Kitchen Cooking Technology, Heating Techniques in the kitchen, Cleaning Techniques in home, Water heating techniques, Ventilation and air conditioning, Home TV and Theatre, Home security etc.
Kitchen technology
- Kitchen Technology – Devices
- Microwave Cooking Principle
- Working Principle of Induction Stove
- How does a Coffee Making Machine work
- Benefits and Use of Pressure Cooker
- Bread Toasters: The Ultimate Convenience in Your Kitchen
- Benefits and Types Chapati Making Machine
Gas Stoves and burner Technology
- Gas stoves and burner technology are widely used in homes due to their efficiency, control, and cost-effectiveness.
- Here’s an overview of gas stove types, burner technologies, and innovations for domestic use:
Gas Stoves Overview
- Types of Gas Stoves:
- Single-Burner Stoves: Compact, often portable, and ideal for small kitchens or outdoor use.
- Double/Triple/Quad Burner Stoves: Common in households, allowing multiple dishes to be cooked simultaneously.
- Built-in Gas Stoves: Installed directly into kitchen countertops, offering a modern look and maximizing space.
- Freestanding Gas Ranges: Feature an oven and stove combination, popular in larger kitchens.
- Biomass Gas Cooking Stoves its advantages and disadvantages
Burner Technology
- Types of Burners:
- Open Burners: Traditional type where the flame is exposed. Provides good visibility and heat but may lead to heat loss.
- Sealed Burners: Have a cover over the flame, directing heat better and making the stove easier to clean.
- Brass Burners: Durable and corrosion-resistant, brass burners provide even heat distribution and are more energy-efficient.
- Aluminum Burners: Lightweight and cost-effective, but they tend to wear out faster than brass.
- Infrared Burners: Use ceramic or metal plates with tiny holes for infrared heat, providing efficient, direct heat with less fuel consumption.
- Specialized Burner Types:
- Simmer Burners: Designed for low-heat cooking, useful for slow cooking or sauces.
- High-Output Burners: Designed for high-heat tasks like stir-frying or boiling, delivering up to 15,000 BTUs or more.
- Multi-Ring Burners: Have multiple rings of flame for better heat distribution, allowing for better control over cooking temperatures.
Key Technologies in Gas Burners for Domestic Use
- Auto-Ignition: Uses electric sparks or batteries to ignite the burner automatically, eliminating the need for matches or lighters. This is both safer and more convenient.
- Flame Failure Protection: An automatic shut-off mechanism detects when the flame goes out and cuts off the gas supply to prevent leaks.
- Thermocouple Safety: A sensor detects when the flame is out and closes the gas valve automatically, ensuring safety against gas leaks.
- Enamel and Glass-Coated Surfaces: These surfaces around the burners make cleaning easier and protect the stove from corrosion.
- Burner and cooking Blog Posts
- Gas stoves and burners continue to evolve with technologies aimed at improving safety, energy efficiency, and convenience for home users.
- These innovations contribute to a more controlled and environmentally friendly cooking experience.
- Working Principle of LPG Gas Stove
- Gas Stove Burners Trouble Shooting and its Solutions
- Popular Gas Stove and Ignitors for Cooking: its Types and Applications
- Best Guide for Non-stick Cookware for Kitchens with Advantages, Disadvantages
- PNG, LPG, and GNG which Gas is Better for Domestic Cooking
- Scope of kitchen thermometer for Efficient and Precision Cooking
- Best Guide for Non-stick Cookware for Kitchens with Advantages, Disadvantages
- How to Select Fruit Blender and Juicer for home
- Best Oil Extraction Machine for Home at Low cost
- Best Burners used in Hotels for Cooking over LPG stoves
Efficiency and Environmental Aspects
- Energy-Efficient Burners: Designed to minimize fuel consumption while maintaining performance. Innovations in burner design, like precision-engineered nozzles and optimized flame patterns, have made modern burners more efficient.
- Low-Emission Burners: Some modern burners are designed to reduce carbon monoxide (CO) emissions, contributing to cleaner indoor air quality.
- Gas-Saving Burners: Certain brands offer designs that use up to 15-20% less gas while achieving the same cooking results.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
- Smart Controls: Some gas stoves now come with smartphone apps or touch controls, allowing remote monitoring of the cooking process or adjustments to the flame.
- Dual Fuel Options: Combination stoves that allow switching between gas and electric cooking modes offer flexibility and ensure continued use even if one fuel source is unavailable.
- Temperature Sensors: High-tech burners with temperature sensors provide precise control, helping to avoid burning food and optimize cooking times.
- Eco-Friendly Alternatives: With an increasing focus on sustainable cooking methods, some manufacturers are developing gas stoves compatible with biogas, which is a cleaner and renewable fuel option.
Safety Features
- Child Lock Controls: Prevents accidental ignition or tampering with the stove.
- Auto Shut-Off Timers: Allows users to set cooking time; the stove will shut off the burner automatically once time is up, useful for longer cooking processes.
- Stabilized Grates: Ensures that pots and pans remain stable on the burner, reducing the risk of spills and accidents.
Solar Energy (heating) Technology
- Solar energy for heating is increasingly being applied in cooking and energy-saving systems, leveraging sustainable, renewable energy for various household applications. Here’s an overview of solar heating techniques, applications in cooking, and ways it promotes energy efficiency:
Solar Cooking Techniques
Solar cooking is an efficient way to utilize sunlight directly for preparing food. The primary types of solar cookers include:
- Box Cookers: Enclosed boxes that trap heat from sunlight, often with a glass lid and insulation. They work like ovens and can slowly cook food over several hours.
- Parabolic Cookers: Use a concave mirror to focus sunlight on a central point, achieving high temperatures quickly for frying and grilling. These are particularly effective for high-heat cooking but require periodic realignment with the sun.
- Panel Cookers: A combination of reflective panels directs sunlight onto a cooking pot inside a plastic or glass enclosure. This type is low-cost and portable, ideal for regions with ample sunlight but low heating needs.
- Solar Concentrators: Advanced versions focus sunlight with mirrors or lenses onto a receiver to achieve very high temperatures. They can be used with heat storage to extend cooking time after sunset.
Solar Heating for Cooking Applications
Solar heating can be integrated into regular cooking routines with some simple technologies:
- Solar-Assisted Ovens: Solar panels or concentrators preheat oven chambers or provide a supplementary heat source for conventional ovens, reducing electricity or fuel consumption.
- Hybrid Solar Cookers: Combine solar energy with electric or gas backup, allowing cooking when sunlight is insufficient. The solar energy stored during sunny hours can be released for cooking later, making these cookers versatile.
- Solar Steam Generators for Cooking: Concentrated solar power (CSP) systems heat water to create steam, which can be used for cooking food directly or for steaming applications. This technique is especially popular in larger, community-based kitchens.
Energy-Saving Solar Heating Techniques
Solar heating techniques extend beyond cooking and can contribute significantly to household energy savings:
- Solar Water Heaters: Collect solar energy to heat water for domestic use. Solar water heaters can save up to 80% of the energy typically used in water heating, which is especially beneficial in sunny regions.
- Thermal Mass and Heat Storage Systems: Some solar heating systems use materials like salt, water, or stones that retain and release heat slowly. This stored heat can be used for evening cooking or maintaining hot water availability overnight.
- Solar Thermal Storage Cooking Systems: These systems use Phase Change Materials (PCMs) to store heat during peak sunlight and release it gradually. This allows cooking and heating during the evening hours, providing flexibility for users.
Benefits of Solar Energy for Cooking and Energy Savings
- Lower Utility Bills: Reduces the need for electricity, gas, or other conventional fuels, lowering overall household energy expenses.
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar cooking and heating replace the need for fossil fuels, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
- Promotes Healthier Indoor Air Quality: Solar cooking doesn’t produce smoke or indoor pollutants, making it safer, particularly in areas where wood or coal are primary cooking fuels.
- Reduces Fuel Dependency: Helps families in remote or underserved areas rely less on expensive or hard-to-source fuels.
- Minimal Maintenance Costs: Solar cookers and heaters typically have few moving parts, resulting in low maintenance costs.
- Benefits of Solar Energy for Home
-
Benefits and Installations of Solar Tunnels for Illuminating Home
-
Eligibility and Benefits of Government Scheme for Free Solar Rooftop
- Working Principle and Benefits of Solar Energy to Heat Swimming Pool
-
Best 10 Solar Lamp for homes, Circuit Diagram and Prices in India
-
Benefits of Solar Water Heater, Storage Capacity, Cost and Installation Guide
- Top 10 Modern Solar Pool Heating Techniques
-
Electricity from Solar Cells for Home: PV Cells and its Selection for Home
Solar Cooking and Heating Applications in Community and Commercial Settings
- Community Solar Kitchens: Larger-scale parabolic or box solar cookers are used in community kitchens to prepare food for large groups, saving costs and providing a sustainable cooking method.
- Solar-Assisted Food Processing: Solar energy is used in drying fruits, vegetables, and other foods, preserving them in an energy-efficient way for commercial use or storage.
- Solar Steam Cooking Systems for Institutions: Schools, temples, and other institutions in sunny regions often use solar concentrators to cook large quantities of food efficiently.
Solar-Powered Appliances for Efficient Cooking
- Solar-Powered Induction Cooktops: Use solar energy to generate electricity for induction cooking, providing efficient heat transfer and cooking without flames or emissions.
- Solar Battery Storage for Appliances: Solar panels store energy in batteries during the day, allowing users to power cooking appliances (like blenders or rice cookers) during evening hours, increasing flexibility in meal preparation times.
- Electricity from Solar Cells for Home
- Solar Cooker for Food
- Advantages and Disadvantages Roof Top Scheme by Government
- Rainwater Harvesting Techniques for home
- Best 10 Solar Lamp for homes, Circuit Diagram and Prices in India
Ventilation and Air Conditioning, Refrigeration Technology
- Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) and Refrigeration Technology are essential for controlling indoor air quality, temperature, and humidity in residential, commercial, and industrial environments. Here’s an overview of each component and key technologies:
Ventilation
- Purpose: Ensures a consistent supply of fresh air indoors, removes contaminants (e.g., CO₂, VOCs, dust), and regulates humidity.
- Types:
- Natural Ventilation: Uses openings like windows, vents, and louvers to allow natural airflow.
- Mechanical Ventilation: Uses fans and duct systems to control and distribute airflow. Common in areas where natural ventilation isn’t effective.
- Key Technologies:
- Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERV) and Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRV): Recover heat or cooling energy from exhausted indoor air to precondition incoming air, saving energy.
- Demand-Controlled Ventilation (DCV): Adjusts ventilation rates based on occupancy levels, improving energy efficiency.
-
Refer the Best ventilation of home in blog posts
- Benefit and installation of Kitchen Chimney
- Selection Kitchen Chimney for Clean Home : Types, Benefit and Installation
-
Best Guides for Kitchen Chimney Installation and Service in Home
- Best Technique for Natural Air Ventilation without AC or Fan
- Effect of Building Colors on Thermal Comfort and Color Guide lines
Air Conditioning
- Purpose: Maintains indoor temperature and humidity at comfortable levels.
- Types:
- Centralized Systems: Use a central unit to cool or heat air, which is then distributed through ducts. Common in larger buildings.
- Split/Multisplit Systems: Have separate indoor and outdoor units. Flexible and efficient for smaller spaces or buildings without existing ductwork.
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) Systems: Enable precise control by varying the flow of refrigerant to multiple indoor units. Ideal for buildings with diverse temperature requirements.
- Key Technologies:
- Inverter Technology: Adjusts compressor speed to meet temperature demands, improving energy efficiency and comfort.
- Smart Thermostats: Allow remote temperature control and scheduling, often equipped with sensors and learning algorithms for optimal performance.
- Refer the ventilation issues of home in blog posts
Refrigeration
- Purpose: Removes heat to lower temperatures, primarily for food preservation, medical, and industrial applications.
- Key Components:
- Compressor: Compresses refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure.
- Condenser: Removes heat from the refrigerant, which then condenses to a liquid.
- Expansion Valve: Lowers the pressure of the liquid refrigerant, cooling it.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the surrounding air or environment, allowing refrigerant to vaporize and continue the cycle.
- Types:
- Residential Refrigeration: Includes home refrigerators and freezers.
- Commercial Refrigeration: For supermarkets, restaurants, and hospitals, requiring high-performance and reliable systems.
- Industrial Refrigeration: Used in warehouses, ice production, and food processing, where larger systems maintain extremely low temperatures.
- Key Technologies:
- Natural Refrigerants: Like CO₂ and ammonia, they have low environmental impact compared to conventional refrigerants.
- Variable-Speed Compressors: Adjust cooling capacity to match demand, saving energy in low-load conditions.
- Thermal Storage Systems: Store cooling energy during off-peak hours for use during peak times, reducing energy costs.
- Water Cooling Technique
- Refer the blog post of refrigeration
Emerging Technologies and Trends
- IoT Integration: Sensors and smart controls for real-time monitoring and remote access.
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Use of renewable energy sources, improved insulation, and eco-friendly refrigerants are rising trends in HVAC and refrigeration.
- CFD Modeling for Optimization: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is increasingly used to design more efficient ventilation, air distribution, and refrigeration systems.
These technologies are essential for maintaining comfort, efficiency, and safety in various environments while also reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
Biomass Energy for Future
- Biomass energy holds significant potential for a sustainable future as it uses organic materials like plant waste, agricultural residues, and animal by-products as fuel.
- Biomass can be converted into electricity, heat, or biofuels, offering a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Here’s a look at how biomass energy could shape the future:
- Which is better either Biomass stove or Induction heating
Types of Biomass Energy Conversion
Biomass can be converted into energy through several primary methods:
- Combustion: Directly burning biomass materials like wood, crop residues, and pellets to produce heat for cooking, heating, or generating electricity.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Breaking down organic waste in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas, which can be used for cooking, heating, or electricity generation. This is particularly useful for managing organic waste in communities and farms.
- Pyrolysis: Heating biomass in the absence of oxygen to produce biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Pyrolysis can yield fuel products with a high energy density and produce biochar, a carbon-rich by-product that can improve soil health and sequester carbon.
- Gasification: Partially oxidizing biomass to produce syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) that can be used to generate electricity or as a base for biofuel production.
- Fermentation: Converting biomass like sugarcane or corn into bioethanol through fermentation. Bioethanol can be used as a fuel or blended with gasoline to reduce carbon emissions.
Biomass as a Source of Clean Energy
- Carbon Neutrality: Biomass is considered carbon-neutral since the CO₂ released during combustion or conversion was absorbed by the plants as they grew. When managed sustainably, it creates a closed carbon cycle, making it an environmentally favorable alternative to fossil fuels.
- Waste Reduction: Biomass energy can utilize agricultural, forestry, and even municipal waste, reducing landfill use and mitigating methane emissions, which is a potent greenhouse gas.
- Sustainable Supply: Unlike fossil fuels, biomass can be continually regenerated through sustainable forestry and agricultural practices, ensuring a long-term supply.
Biofuels for Transportation
Biomass-derived biofuels, such as bioethanol and biodiesel, offer promising solutions for the transportation sector, especially for industries like aviation and shipping, where battery-powered solutions are less feasible.
- Bioethanol: Typically made from sugar- and starch-rich crops like corn and sugarcane, bioethanol is blended with gasoline to reduce emissions. It is also adaptable to second-generation sources, such as cellulosic materials (e.g., crop residues and grasses).
- Biodiesel: Produced from vegetable oils or animal fats, biodiesel can replace or supplement diesel in engines. It’s biodegradable, non-toxic, and produces significantly lower emissions than petroleum diesel.
- Advanced Biofuels: Ongoing research focuses on converting algae and other non-food crops into biofuels, which do not compete with food resources and can be cultivated on non-arable land.
- Best Charcoal Making Methods from Biomass in Farms
Biomass in Electricity Generation
Biomass can be used to produce electricity through direct combustion, co-firing in coal plants, or through biogas-fueled turbines. Biomass electricity generation has particular advantages:
- Baseload Power: Unlike solar or wind, which are intermittent, biomass can provide continuous power, making it suitable for baseload generation.
- Grid Stability: Biomass power plants can help balance grids with high renewable penetration, as they can adjust output more easily than solar or wind power.
- Localized Generation: Biomass plants can be set up near the source of biomass, reducing transportation costs and providing energy to local communities.
Biomass for Heating and Cooking
- Rural Cooking Solutions: In rural areas where access to electricity is limited, biomass cookstoves provide an affordable cooking solution while reducing indoor air pollution when designed to be smokeless.
- District Heating: Biomass can also be used in district heating systems, where it generates heat for entire communities, reducing reliance on natural gas or oil.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
- Reduced Dependency on Fossil Fuels: Biomass offers an alternative energy source that can help reduce reliance on coal, oil, and natural gas, especially for rural and agricultural communities.
- Job Creation: Biomass energy promotes job opportunities in agriculture, forestry, waste management, and the energy sector.
- Soil Enrichment: The biochar produced from pyrolysis can improve soil fertility and water retention, contributing to more sustainable agricultural practices.
Future Innovations and Research in Biomass
- Second-Generation Biofuels: Researchers are developing methods to convert non-food biomass sources, such as crop residues, grasses, and algae, into biofuels, which do not compete with food supply.
- Algae Biomass: Algae have a high yield potential and can be cultivated on non-arable land, making them a promising biofuel source. Algae-based biofuels are also rich in lipids, which can be converted into biodiesel.
- Biomass Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS): By capturing CO₂ emissions from biomass power plants and storing it underground, BECCS can make biomass energy carbon-negative, actively removing CO₂ from the atmosphere.
- Biomass blog posts
-
-
What are the sources of energy in rural India in the future?
- Benefits of Biogas Gas Plant for Homes
- Scope of Biomass Energy in Rural Areas of India
-
Scope of Biomass Stoves for Cooking Its Advantages and Disadvantages
-
Biomass Briquetting Machines: Parts, Raw Materials, Cost and Efficiency
-
Scope of Biomass Briquette Stoves for Cooking: Advantages, Applications and Types
-
Scope of Biomass Pellet Making Machine: its type and applications
-
Performance Evaluation of Biomass Stove: Efficiency Calculations and Emissions Predictions
- Controlling Emissions from Biomass Stoves: A Path to Cleaner Cooking
-
Smoke and Dust Minimization Techniques for Briquette and Pellet Stoves
-
Best Tandoors Oven for Cooking in Restaurants: Types, Advantages and Applications
- Scope Charcoal Briquette For Cooking: Advantages, Cost and Production
- Modern 7 Smokeless Biomass Cooking Methods in kitchen
- Best Burners used in Hotels for Cooking over LPG stoves
- Benefits and Types of Charcoal Barbecue Grills for Efficient Cooking
-
Biomass Heating Calculation
- Biomass Heating Value Calculation of Bamboo Pellet
- Which Biomass is the Best for Hotels and Cooking
- Which is better either Biomass stove or Induction heating
- How to Select Best Charcoal in Stoves for Cooking
- Effect of Difference Biomass on Thermal Efficiency of Furnace
-
Best Practice to Prevent Dust Entering into Your Home
Electrical Vehicles and Battery Technology in Homes
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and battery technology are increasingly becoming integrated into home environments, creating new opportunities for energy management, sustainability, and efficiency.
- EVs and home batteries can provide backup power, reduce electricity costs, and even support the grid. Here’s a breakdown of the roles EVs and battery technology can play in the home:
EV Charging at Home
- Types of EV Chargers:
- Level 1 Charger: A standard 120V plug that provides slow charging (about 3-5 miles of range per hour) and can be used with existing home outlets.
- Level 2 Charger: A 240V charger that typically requires a dedicated circuit. Level 2 chargers are faster, adding about 15-30 miles of range per hour, and are the most common choice for home charging.
- Smart Chargers: Some Level 2 chargers come with smart features that allow for scheduling, energy monitoring, and remote control through smartphone apps.
- Installation Considerations: Installing a Level 2 charger may require upgrades to the home’s electrical system, especially if the home has an older panel or limited capacity.
- Time-of-Use Charging: Many utilities offer time-of-use rates, where electricity is cheaper during off-peak hours (like overnight). EV owners can save by charging their vehicles during these periods.
Bidirectional Charging (Vehicle-to-Home)
- How it Works: Bidirectional chargers enable electricity to flow both ways, allowing EVs to act as backup batteries for the home. Known as vehicle-to-home (V2H) or vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, this approach provides additional power flexibility.
- Backup Power: During a power outage, EV batteries can supply power to essential home appliances, providing hours or even days of backup electricity, depending on the battery size and home energy consumption.
- Energy Cost Management: Some EV owners use bidirectional charging to charge the car battery during off-peak times and discharge it during peak times when electricity costs more. This approach reduces energy bills and helps balance grid demand.
- System Compatibility: Not all EVs and chargers support bidirectional charging, but models like the Nissan Leaf and the Ford F-150 Lightning have introduced this feature.
. Home Battery Storage Systems
- Purpose and Functionality: Home battery systems, like Tesla Powerwall, LG Chem, and others, store electricity from solar panels or the grid. They provide backup power, manage peak electricity usage, and enhance energy self-sufficiency.
- Integration with Solar Power: Pairing home batteries with solar panels allows excess solar energy to be stored and used later, minimizing grid dependence and making the home more resilient to outages.
-
- How to Select the Best Electric Vehicle Car
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Ola S1 Pro with User Experience
- Best 5 Electric scooters in India in 2024 for Home
- How to select Electric Vehicle (EV) – Scooty
-
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ola S1 Pro with User Experience
-
How to Prevent Fires from Battery in Electrical vehicles with Blanket
- Best 10 Tips to Increase the Battery Life of Electric Scooter
-
Best 5 Electric Scooters in India in 2024 for Home- User Experience
-
How to Prevent the fire from Electric Vehicles in Hot Summer in India
- 10 Best Electric Scooter to Buy in Festivals with Key Features
Cleaning Technique in Home
Effective home cleaning involves various techniques that keep living spaces sanitary, safe, and comfortable. Different areas of the home require unique approaches based on surfaces, materials, and level of dirt or clutter. Here are some fundamental cleaning techniques and tips for maintaining a clean home:
- Working Principle of Washing Machine and its types
- Can Dish Washer Machine clean Utensils
- Why Vacuum Cleaner is the best for Dust removal
-
Best Hand Wash Dispenser for Bathroom and Home, Types and Design
-
Benefits of Kitchen Dishwashing Soap Dispensers: Types and User Guide
-
-
Best Tips For Cleaning Kitchen and Methods to Remove to Dust
- User How to Minimize Food Waste in Kitchen
Water Heating Technique
- Working Principle of Electric Geyser
- Immersion Water Heater and its fixing and Safety precautions
- Solar Water Heating and its benefits
-
Best Safety Tips for Shockproof Water Geyser and Immersion Heater
- Rainwater Harvesting Techniques for home
Essential Electrical Appliances in Home
- Battery Inverter for Home
- How to make Drone in Home and Government Regulation
- Innovative Battery Designs for Chemistry, Types and Applications
- Advantages and Disadvantages, Details of Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) for polling
- Benefits and Use of Electric Mixers for Cooking
-
Immersion Water Heater: Types, Parts, Advantage and Safety Precautions
-
Working Principle of Electric Geyser: Benefits, Parts and Types
Home security and safety Tips
Food Preservation and Drying Methods
- Working Principle of Home Refrigerator
- Food Drying Techniques at Home
- Food Preservation Techniques in Home
Food Safety and Waste Management
Home TV Theatre and Music
Laptop Computer and Electronics
- which one is better laptop or a desktop?
- Major Issues on Desktop and CPU: How to Prevent Overeating, Dust Collection
- How to Select Best Laptop for Different Engineering Students
- Best Laptop To Buy 2023
- Types and Applications Data cables for Laptop, PC and Mobiles
- Types and Applications Data cables for Laptop, PC and Mobiles
- Best Graphics Cards and Issues in GPU in Your Computer and workstations
- Best Laptop To Buy 2023
Best Buy Items for Homes
- Best Essential Stationery Items for Homes and Offices
- Essential Baby Products for Value for Money
- Best Buy for Babies Carrier Bags from Big Billion Sales
- Essential Baby Products forBest Value for Money
Home construction Technique
- Best Waterproofing Techniques and its Importance for Homes
-
Building a Sustainable Future: Embracing Green Building Practices
Water Filtration Techniques and Water Hardness Measurement
Smart Phone Technology
- Best Phone in Market 2024 for Camera and Specifications In India
-
Advantages and Disadvantages of Popular Curved Phones in the Market
-
Best Camera Quality Mobiles under Rs 20000 in India in 2023 based on Review
- Advantages and disadvantages of Popular Foldable Smartphone
Best Mobile Technology
-
-
Best Camera Quality Mobiles under Rs 20000 in India in 2023 based on Review
- Oppo Reno 12 5G is Best AI Camera Phone Compared to I phone 15 Max
-
Refurbished Phone Steps-Pros and Cons Buying and Common Issues
-
Best Phone in Market 2024 for Camera and Specifications In India
-
Advantages and Disadvantages of Popular Curved Phones in Market
Food Technology
- Best Ideas for Waste Recycling to Best Products in Home
-
Best Organic Jaggery Making Methods and Prevention of its adulteration
Waste Recycle, and Decoration Ideas in Homes
Gallery of Posts
Home Technology for Effective and Safe

Comparison of Kitchen Chimney and Exhaust Fan for Ventilations

Which Kitchen Chimney is Better with or without Ducts

Low Cost Kitchen Chimney Selection

Issues and Common Mistakes in Kitchen Chimney Selection
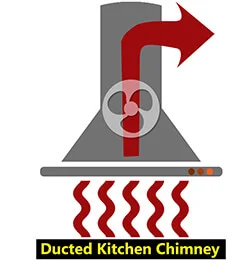
Kitchen Chimney Design and Selection Guidelines

Best Chimney for Kitchen and Hotels and Restaurant

Best Practice to Prevent Dust Entering into Your Home

Effect of Building Colors on Thermal Comfort and Color Guide lines

Thermal Comfort Design for Modern Building

15 Modern Energy Efficient and Clean Cooking Methods

Benefits of and Parts Kitchen Chimney with its Types

Best Technique for Natural Air Ventilation without AC or Fan

PNG, LPG and CNG which Gas is Better Cooking and Gas Conversion Guides

Best Guide for Non-stick Cookware for Kitchens with Advantages, Disadvantages

How to Select Best Vacuum Cleaner for Cars

Best Tips For Kitchen Cleaning Methods and Dust Removals

Best Potato Chips Making Machine for Home

Best Hand Wash Dispenser for Bathroom and Home, Types and Design

Benefits of Kitchen Dishwashing Soap Dispensers: Types and User Guide

Scope of kitchen thermometer for Efficient and Precision Cooking

Best Guides for Kitchen Chimney Installation and Service in Home

Gas Stove Burners Trouble Shooting and its Solutions
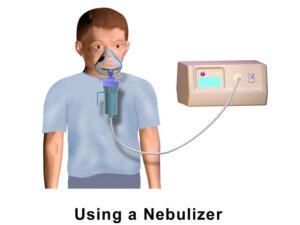
How to Use Nebulizer for Cough in Home: Parts of Nebulizer

Washing Machines Trouble Shootings and its Solution in Home

Major Cooling Problems in Air Conditioners and Solutions to Trouble shooting

Fire Safety Tips in Kitchen: Prevention of risks

Best Wiper for All Purpose Cleaning in Home

Best Cleaner for Tiles in home

Popular Gas Stove and Ignitors for Cooking: its Types and Applications

Benefits and Types Chapati Making Machine

Design of Jaggery Furnace Plant Using Biomass

How to Select Best Charcoal in Stoves for Cooking

Effect of Biomass on Thermal Efficiency of Furnace

Biomass Heating Value Calculation of Bamboo Pellet
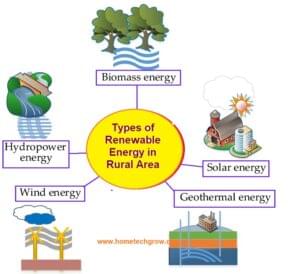
Solar energy or Biomass Which is Better for Rural Areas
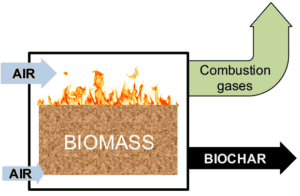
Scope of Carbonization Process for Biomass in Rural Areas

Best Charcoal Making Methods from Biomass in Farms

Which Biomass is the Best for Hotels and Cooking

Which is better either Biomass stove or Induction heating

Biomass Stove Engineering Design Guide and Calculations
EV Technology for Home
Biomass Energy









