Biomass Pellet Stoves
- A biomass pellet stove is a type of heating appliance that uses biomass pellets as its primary fuel source to generate heat.
- It operates on the same principle as a traditional wood pellet stove but utilizes biomass pellets made from various organic materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and other biomass sources.

The heating value of a Biomass Pellet
- Pellet stoves have heating capacities that range between 8,000 and 90,000 Btu per hour
- The calorific value of wood pellets is approx. 18,17 MJ/kg.
- HHV is the efficiency rate recognized by the EPA.
- The wood used inside when testing a wood stove needs to be between 19% and 25% moisture content, which is a real-world scenario when burning wood at your own personal house.
- LHV is a theoretical number where the stove is tested using 0% wood moisture
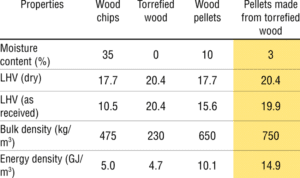
Comparison of Pellet heating value with other wood
- Wood pellets and wood both have heating value, which refers to the amount of heat energy they can produce when burned.
- The heating value is typically measured in British thermal units (BTUs) per unit of weight (e.g., per pound or per kilogram).

- The comparison between the heating value of wood pellets and wood can depend on various factors, such as the type of wood, the moisture content, and the density of the material. Here’s a general comparison:
Heating Value of Wood:
- The heating value of wood can vary widely depending on the species of wood and its moisture content. Dry wood typically has a higher heating value than green or wet wood.
- On average, dry hardwoods have a heating value of about 24 to 27 million BTUs per cord (a cord is a stack of wood that measures 4 feet high by 4 feet wide by 8 feet long). This is equivalent to approximately 6,800 to 7,900 BTUs per pound.
- Softwoods generally have a slightly lower heating value than hardwoods, ranging from 20 to 24 million BTUs per cord or around 5,600 to 6,800 BTUs per pound.
Heating Value of Wood Pellets:
- Wood pellets are a manufactured form of wood made by compressing wood particles or sawdust. They have a more consistent moisture content and density compared to raw wood, which can result in a higher heating value.
- The heating value of wood pellets typically ranges from 8,000 to 8,600 BTUs per pound, depending on the quality and type of wood used in their production.
- High-quality wood pellets made from hardwood can have a slightly higher heating value compared to those made from softwood.
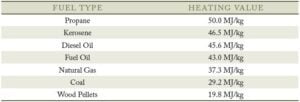
Overall, wood pellets generally have a higher heating value per unit weight compared to raw wood. This increased efficiency can be attributed to the controlled manufacturing process, uniform density, and lower moisture content of wood pellets. However, the choice between using raw wood or wood pellets for heating purposes also depends on factors like availability, cost, and the specific heating appliance being used.
Major parts of Biomass Pellet Stove
Biomass pellet stoves consist of many mechanical parts. Based on commercial practices the following are major parts
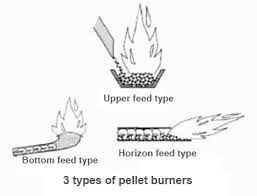
- Burner
- Biomass feeding
- Air Draft
- Forced
- Natural
- Ash handling system
- Ceramic coating
- Casing of furnace
- holding of furnace
- Exhaust system
- Open space
- chimney exhaust

- A biomass briquette machine is used to produce the pellets.
- You can refer to the post what are the process involved in making pellets.
- Biomass pellet stoves are a type of heating appliance that uses biomass pellets as a fuel source to generate heat for residential and commercial spaces. These stoves are considered a more environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional wood-burning stoves and fossil fuel-based heating systems.
Biomass pellets:
- Biomass pellets are small, cylindrical pellets made from compacted organic materials.
- Common biomass sources for pellets include wood, agricultural residues, and other organic materials.
- The pellets have a uniform size, shape, and moisture content, which contributes to their efficient combustion.
Pellet Hopper
- The pellet stove has a hopper that stores the biomass pellets.
- The hopper capacity can vary depending on the stove’s size, but it typically holds enough pellets to provide heat for several hours or even days, depending on the stove’s settings and the outside temperature.

Feeding Mechanism
- A motorized auger or feeding mechanism is used to transfer the biomass pellets from the hopper to the combustion chamber.
- The rate at which the pellets are fed into the combustion chamber can usually be adjusted to control the heat output.

Combustion Chamber
- The combustion chamber is where the biomass pellets burn and release heat.
- The stoves are designed to ensure efficient combustion and minimal emissions.
- Some models may also have secondary combustion zones to further reduce particulate emissions.
Ignition and Control System
- Pellet stoves usually have an automated ignition system that starts the combustion process.
- They also come equipped with control panels or remote controls that allow users to adjust the temperature and heat output as needed.
Heat exchanger and fan:
- The heat generated during combustion is transferred to the surrounding air through a heat exchanger.
- A fan helps distribute the heated air into the room, providing warmth and creating a comfortable indoor environment.
Air Circulation
- A fan within the pellet stove facilitates the circulation of air over the heat exchanger.
- The heated air is then blown into the room or space, providing warmth and increasing the indoor temperature.
Exhaust System
- As a result of combustion, some byproducts and waste gases are produced. These include carbon dioxide, water vapor, and small amounts of particulate matter. The stove is equipped with an exhaust system that vents these byproducts and emissions outside, usually through a vent pipe or chimney.
Fuel Control system:
- Most modern biomass pellet stoves are equipped with control panels that allow users to adjust various settings, such as the heat output, the rate of pellet feeding, and even programmable timers for automatic operation.
- These control systems make the operation of the pellet stove user-friendly and convenient.

Advantages of biomass pellet Stoves
- Renewable energy: Biomass pellets are made from sustainable and renewable organic materials, making them an environmentally friendly heating option.
- Efficiency: Pellet stoves are highly efficient, with combustion processes designed to extract the maximum amount of heat from the pellets, resulting in a more effective heating system.
- Low emissions: Biomass pellets have a consistent composition and burn more cleanly than some other biomass fuels, leading to lower emissions and reduced environmental impact.
- Convenience: Pellet stoves are relatively easy to use and can be automated to a certain extent. Many models come with programmable thermostats and remote controls for added convenience.
- Cost-effective: In some regions, biomass pellets can be more cost-effective compared to other heating options, especially if biomass materials are readily available.

Is a pellet stove better than a wood stove?
Whether a pellet stove is better than a wood stove depends on various factors, including your specific needs, preferences, and local circumstances. Let’s compare the two types of stoves to help you make an informed decision:
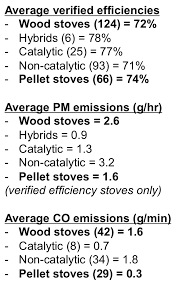
High Efficiency
-
- Pellet stoves are generally more efficient than traditional wood stoves.
- They use compressed and uniform biomass pellets, allowing for a more controlled and efficient combustion process.
- Wood stoves, on the other hand, may have varying wood types and moisture levels, which can affect their efficiency.
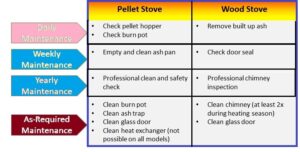
Ease of Use
-
- Pellet stoves are easier to use and can often be automated.
- They typically have a hopper that automatically feeds pellets into the combustion chamber, and many models come with programmable thermostats and remote controls.
- Wood stoves require manual loading of firewood and may need more frequent tending to maintain a consistent burn.
Fuel availability and storage:
-
- Wood stoves rely on firewood, which may be readily available in certain areas, especially in rural locations.
- However, you need space to store firewood properly, and it requires seasoning to achieve optimal burning efficiency. Pellets, on the other hand, are widely available and can be purchased in bags, making storage easier and cleaner.
Less Environmental impact
- Both pellet stoves and modern wood stoves can be environmentally friendly options when it comes to heating.
- Pellet stoves burn biomass, which is considered carbon-neutral since the carbon dioxide emitted during combustion is equivalent to the amount absorbed by the plants during growth.
- Wood stoves can also be environmentally friendly if they are EPA-certified and burn seasoned firewood with low moisture content.

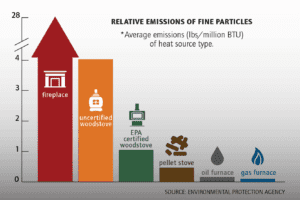
Low Emissions
- Pellet stoves generally produce lower emissions and less particulate matter compared to traditional wood stoves.
- Modern wood stoves, especially those meeting EPA emission standards, have also made significant progress in reducing emissions.
Convenience:
- Pellet stoves often provide a more consistent and controllable heat output, thanks to their automated systems.
- Wood stoves require more manual effort to maintain a steady heat level.
Cost
- The cost of operating a pellet stove versus a wood stove can vary depending on the local availability and cost of pellets and firewood.
- In some regions, pellets may be more cost-effective than firewood.
Aesthetics:
- Some people prefer the ambiance and crackling sounds of burning firewood in a traditional wood stove, while others appreciate the clean and efficient operation of a pellet stove.
Summary
- In summary, if you prioritize convenience, automated operation, and higher efficiency, a pellet stove might be a better choice for you.
- On the other hand, if you have easy access to affordable firewood and enjoy the traditional charm of a wood-burning stove, you may prefer a wood stove. Additionally, considering the environmental impact and emission levels of both options is crucial in making an environmentally conscious decision.
- Despite their advantages, it’s essential to consider the availability of biomass pellets in your area and the stove’s maintenance requirements when deciding whether a biomass pellet stove is the right heating solution for your needs

It is quiet acceptable but what about pittete biomass cost