Why should use Filtered Water for Home
- Water is a fundamental component of life, and we need it for many purposes such as drinking, cooking, cleaning, and irrigation
- However, not all water sources are clean and safe for consumption, as they may contain impurities such as bacteria, viruses, chemicals, and sediments
- Therefore, it is crucial to have water filtration techniques that can remove or reduce these contaminants to make water safe and healthy for human and environmental use.
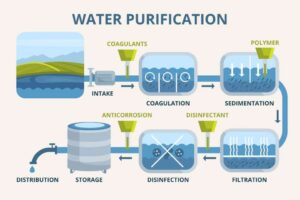
Common water filtration technique
In this blog post, we will discuss some of the most common water filtration techniques and how they work.
- Ceramic Filtration
- Sediment filtration
- Activated carbon filtration
- Reverse osmosis filtration
- UV disinfection
- Distillation
- Ozonation
- Ion Exchange Filtration
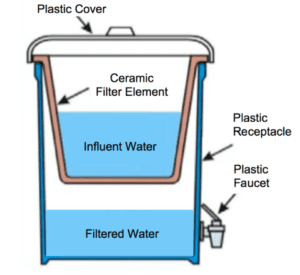
Ceramic Water Filtration
- Ceramic filters are less inexpensive
- Its effectiveness of filtration depends on pore size in ceramic material to filter debris, dirt and bacteria out of water
- This is an ideal choice for low-budget users
- Portable ceramic filters are commonly used in backpacking.
- Ceramic water filters can achieve ultra-fine filtration
- This is why they are so effective at removing cyst parasites and incapacitating bacteria
- Material of Filter: The ceramic filter is made out of aluminum oxide, silica oxide, and silica carbide.

- Ceramic filters can give a high dust removal efficiency
- Many people use mud pots for water storage which can settle impurities
- The ceramic acts as a good thermal insulator due to its porosity
- The effect of extreme changes in temperature on the water is less
- Filtration Efficiency:
- The average removal efficiency of the ceramic filters varies from 60% to 90%.
- It depends on the porosity of ceramic materials
Sediment Filtration
- Sediment filtration is the most basic and common water filtration technique that is used in many homes and industries
- It involves passing water through a physical barrier that traps particles and impurities such as sand, silt, and rust
- Sediment filters can be made of various materials, including paper, cloth, and mesh screens, and they come in different sizes and shapes
- Some sediment filters are disposable and need to be replaced periodically, while others are washable and reusable.

- The advantage of sediment filtration is that it is simple, affordable, and effective in removing large particles from water
- However, it may not be sufficient to remove smaller particles, such as bacteria and viruses, which can pass through the filter.
Activated Carbon Filtration
- Activated carbon filtration is another popular water filtration technique that is used to remove organic contaminants, such as chlorine, pesticides, and solvents
- Activated carbon is a porous material that has a large surface area, which makes it effective in adsorbing (not absorbing) impurities from water.
- When water passes through an activated carbon filter, the organic molecules adhere to the carbon pores and get trapped, leaving the water cleaner and clearer.

- The advantage of activated carbon filtration is that it is easy to use, has a long lifespan, and does not require electricity or chemicals.
- However, it may not be effective in removing inorganic contaminants, such as minerals, salts, and heavy metals.
- Activated carbon filtration (ACF) is a popular water treatment technique that uses activated carbon to remove impurities and contaminants from water
- Activated carbon (ACF) is a form of carbon that has been treated with oxygen to create tiny pores between carbon atoms. These pores create a large surface area that can adsorb (not absorb) impurities, such as organic compounds, chlorine, and sediment.
- The ACF process involves passing water through a bed of activated carbon, which traps the impurities and produces a clean, clear, and odorless water
- The filtration process can be passive or active, depending on the type of filter used. Passive filters are typically made of granulated activated carbon (GAC) and rely on gravity or pressure to force water through the filter
- It uses a pump to create a pressure gradient that pushes water through the filter
- Activated carbon filters are commonly used in household water treatment systems, such as pitchers, faucet-mounted filters, and under-sink filters
- They are also used in larger-scale applications, such as municipal water treatment plants, industrial processes, and wastewater treatment.
Benefits of activated carbon filtration
- Effectiveness: Activated carbon filters can remove a wide range of impurities from water, including chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, herbicides, and sediments. They can also improve the taste and odor of water by removing organic compounds that cause foul smells and tastes.
- Affordability: Activated carbon filters are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. They require minimal maintenance, and the filters can be easily replaced when they become saturated with impurities.
- Environmentally friendly: Activated carbon filters do not use chemicals or produce wastewater, making them an environmentally friendly water treatment option. They also reduce the need for bottled water, which can help reduce plastic waste.
Disadvantage of Activated Carbon Filtration
- Ineffectiveness against inorganic compounds: Activated carbon filters are not effective in removing minerals, salts, and heavy metals from water, which may require additional treatment techniques.
- Short filter lifespan: The filter lifespan of activated carbon filters can vary depending on the type and quality of the filter, as well as the level of impurities in the water. Over time, the filter can become saturated with impurities and lose its effectiveness.
- Bacterial growth: If not properly maintained, activated carbon filters can become a breeding ground for bacteria, which can contaminate the water.
In conclusion, activated carbon filtration is an effective and affordable water treatment technique that can improve the quality and safety of water for human and environmental use. It is a popular choice for household and small-scale applications, but may not be sufficient for large-scale water treatment needs or removal of certain impurities. Regular maintenance and replacement of filters are crucial to ensure the effectiveness and safety of activated carbon filtration systems.
- The activated carbon filtration plant consists of two tanks

Reverse Osmosis Filtration
- Reverse osmosis filtration is a more advanced and complex water filtration technique that is used in industrial and commercial applications, such as desalination and water treatment plants
- It involves passing water through a semi-permeable membrane that allows only water molecules to pass through and traps all other impurities
- Reverse osmosis can remove up to 99% of dissolved solids, such as salts, minerals, and metals, as well as bacteria and viruses.
- The advantage of reverse osmosis filtration is that it can provide high-quality water that is free from most contaminants, including those that are invisible to the naked eye
- However, this technique consumes a large amount of energy. It would be expensive to install and maintain for large-scale levels.

Principle of Reverse osmosis (RO)
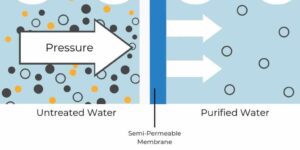
- Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water treatment process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove impurities from water
- The principle of reverse osmosis is based on the natural process of osmosis, which is the movement of water from an area of low concentration of dissolved salts (or solutes) to an area of high concentration of dissolved salts through a semi-permeable membrane
- In reverse osmosis, the process is reversed by applying pressure to the high-concentration side of the membrane, which forces the water to flow in the opposite direction, from the high-concentration side to the low-concentration side, leaving behind the impurities
- The semi-permeable membrane used in reverse osmosis is made of a thin layer of material, usually composed of polymers, that has small pores or channels that allow water to pass through, but not larger particles or dissolved solids. When water is pushed through the membrane under pressure, the impurities, such as dissolved minerals, salts, and organic compounds, are left behind on the high-concentration side of the membrane
- The purified water that passes through the membrane is collected and used for various purposes.
- The RO water filter is shown below

- Reverse osmosis is used for a variety of applications, including desalination of seawater, purification of drinking water, and treatment of wastewater
- It is an effective and efficient way to remove impurities from water, but it does require significant energy to operate and can produce a significant amount of wastewater
- This is the most widely used method to purify water as Membrane technology
- The RO method removes almost all dissolved salts, bacteria, and other impurities from the contaminated water
Advantages of Reverse Osmosis (RO) Filtration
This method has been widely used in many countries. Benefits of RO water are given below.
-
High water filtration efficiency of up to 99%
-
The semipermeable membrane block all particles, and contaminants.
-
Low mechanical maintenance
-
Provide clean and pure water
-
Compact filtration system and requires a small space.
-
Long-life membrane (more than two years)
-
No need for chemicals to purify water
-
Low power consumption
-
The RO systems can be fully automated
Disadvantage of reverse osmosis water
-
Possibility of clogging the whole system which can lead to overflow
-
Need regular filter changes for maintenance.
-
The high installation cost
-
Slow filtration process. Hence you can not more purified water initially
-
RO system can not help in disinfecting the water. Hence, you need to install a separate process to disinfect the water.
-
High hard water (> 1500 ppm) can damage the membrane.
-
A damaged membrane can lead to leakage of small microorganisms passing into drinking water
-
Need more applied pressure with an external pump for the continuous supply of water
-
The RO system may not be self-sustaining
-
They remove most of the minerals from the water leaving it with an acidic pH
- Some water is waster during the purification process
Ultrafiltration (UF) Membrane Filtration
- Ultrafiltration (UF) is a membrane filtration process that separates particles and molecules from a liquid by using a semipermeable membrane. It is an effective method for purifying water, separating proteins, and concentrating substances. UF is commonly used in many industries, including food and beverage, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment
- The process of UF works by using a semipermeable membrane with pore sizes between 0.001 to 0.1 microns. The membrane acts as a filter, allowing water and small molecules to pass through while blocking larger particles and molecules
- The size of the pores in the membrane determines the size of the particles that can be filtered out
- UF is different from other filtration processes, such as microfiltration and nanofiltration, in that it can effectively remove particles and molecules that are too small to be removed by conventional filtration methods. UF can remove particles and molecules such as viruses, bacteria, colloids, proteins, and organic compounds.

Application of UF
UF can be used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Water Treatment:
- UF is an effective method for removing suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses from water
- It is commonly used in the production of drinking water, wastewater treatment, and industrial water treatment.
- Food and Beverage Industry:
- UF can be used for separating and concentrating proteins, enzymes, and other molecules in the food and beverage industry
- It is commonly used for the production of dairy products, fruit juices, and beer.
- Biotechnology and Pharmaceutical Industry:
- UF can be used for separating and purifying proteins, enzymes, and other molecules in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries
- It is commonly used in the production of vaccines, antibodies, and other therapeutic proteins.
- Chemical Industry: UF can be used for separating and concentrating various chemicals and compounds in the chemical industry.

Advantage UF
- Ultrafiltration (UF) is a membrane filtration process that has several advantages over other filtration methods. Here are some of the advantages of ultrafiltration:
- High removal efficiency:
- UF can remove particles and molecules as small as 0.001 microns
- This makes it highly effective in removing suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, colloids, proteins, and other organic compounds from liquids.
- Low energy consumption: UF requires relatively low energy compared to other filtration methods. This is because it operates at lower pressures and does not require high temperatures or chemicals to operate.\
- Environmentally friendly: UF is an environmentally friendly filtration method because it does not produce any harmful waste products. It also requires fewer chemicals and energy than other filtration methods
- Cost-effective: UF is a cost-effective method of filtration because it requires minimal maintenance and has low operating costs. It can also be easily scaled up for larger applications
- Flexible and Versatile: UF can be used in a variety of applications, including water treatment, food and beverage processing, biotechnology, and pharmaceuticals. UF membranes can be designed to meet specific filtration requirements and can be easily integrated into existing production processes
- High Flow Rates: UF membranes have high flow rates, which means they can process large volumes of liquids quickly and efficiently. This makes UF a good choice for applications where high throughput is required.
- Overall, ultrafiltration is a highly effective and versatile method of filtration that offers several advantages over other filtration methods. It is cost-effective, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly, making it a popular choice for many industries.
Ultraviolet (UV) disinfection
- UV disinfection is a water filtration technique that is used to kill or inactivate bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that may be present in water
- It involves exposing water to a UV light source that emits high-energy radiation that damages the DNA of microorganisms and prevents them from reproducing. UV disinfection does not remove particles or impurities from water, but it can make it safe and healthy for consumption

- The advantage of UV disinfection is that it is fast, efficient, and chemical-free
- It does not alter the taste, color, or odor of water and can be used in combination with other filtration techniques to provide a comprehensive water treatment solution.
Which water Purification Technology is the best
- The selection of water filter depends on the quality and source of your water, you can choose a water purifier that is customizable for you
- The Reverse Osmosis (RO) purification technology works best for water with higher total dissolved solids (TDS) levels of more than 500 ppm
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) filters fine heavy metals, dust particulates, and minerals through the selectively permeable membranes and provides purified water
- If water hardness (TDS) is less than 200 ppmv, you should choose the Ultra-Violet (UV) filtration technology which can remove hardness and impurities but retain healthy minerals.
- Water filtration technology is used in various applications, including household, commercial, and industrial settings
- The type of filtration technology used depends on the specific water quality concerns and the desired level of water purity.
-
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Filtration: This is a method that uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter out impurities and contaminants from water.
- Ultraviolet (UV) Filtration: This is a method that uses UV light to kill microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
- Activated Carbon Filtration: This is a method that uses activated carbon to absorb impurities and contaminants from water.
- Distillation: This is a method that involves heating water to produce steam, which is then collected and condensed to produce clean water.
- Ceramic Filtration: This is a method that uses ceramic filters to remove impurities and contaminants from water.
- Ion Exchange Filtration: This is a method that uses resins to remove ions such as calcium and magnesium from water.
- Ozonation: This is a method that uses ozone gas to kill bacteria and viruses in water
- Ultrafiltration (UF): It is a membrane filtration process that has a wide range of applications in various industries. It is an effective method for purifying water, separating proteins, and concentrating substances. UF is a cost-effective, environmentally friendly method that can be easily scaled up for larger applications
Summary
- In conclusion, water filtration techniques are essential to ensure the safety and quality of water for human and environmental use
- The choice of filtration technique depends on the type and level of contaminants in water, as well as the intended use and budget
- Sediment filtration, activated carbon filtration, reverse osmosis filtration, and UV disinfection are some of the most common and effective water filtration techniques that can be used