Scope of Biomass Briquette Stoves
- In today’s rapidly changing world, the pursuit of sustainable energy solutions is more critical than ever.
- Enter biomass briquette stoves, a remarkable innovation that utilizes compact blocks of organic material to provide efficient, clean, and renewable energy for cooking and heating.
- In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating realm of biomass briquette stoves, exploring their benefits, applications, and the role they play in shaping a greener future for our planet.
- Biomass briquettes are a testament to human ingenuity, a transformation of various forms of organic waste into a valuable energy source.
- The process involves compressing biomass materials such as wood residues, agricultural waste, and even paper into dense, solid briquettes. These briquettes possess a high energy density, making them an ideal alternative to traditional firewood and fossil fuels.

Heating value of Biomass Briquette
- The heating value is higher,
- It ranges from 3800-4200 Kcal/kg
- It is equivalent to B-grade coal (4000 Kcal/kg). Biomass Briquette has a higher practical thermal value.
- Low ash content at 5-8% as compared to coal 25 – 45%. Have a consistent quality, have high burning efficiency.
- Charcoal briquette has a high heating value of around 6000-7000 Kcal/kg as mentioned in the post
What are the different types of biomass Briquette cookstoves
Classification of cookstoves
- Three-stone fire 2. Early ICS (Improved Cook Stoves) to 1990s (clay/ceramic/buckets)
- Fuel-controlled stoves (mainly Rocket stoves) – Simple (portable) – Stationary (with chimney)
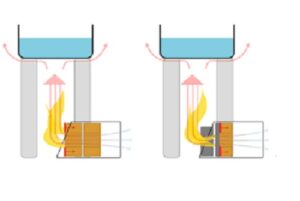
Natural-air Briquette Cookstoves
- In the realm of sustainable cooking solutions, natural-air biomass briquette cookstoves stand as a testament to the beauty of simplicity.
- These stoves harness the power of natural convection and air movement to efficiently burn biomass briquettes, offering an eco-friendly alternative for cooking.
- In this article, we’ll delve into the world of natural-air biomass briquette cookstoves, exploring their principles, benefits, and how they’re making a positive impact on both the environment and daily cooking routines.

Understanding Natural-Air Biomass Briquette Cookstoves:
- Natural-air biomass briquette cookstoves, also known as “convection stoves,” operate on the principle of natural convection.
- Unlike forced-air stoves that use fans to enhance combustion, these stoves rely on the natural movement of air driven by temperature differences.
Key Features of Natural-Air Biomass Briquette Cookstoves:
- Convection Channels: These stoves are designed with carefully engineered convection channels that facilitate the movement of air. These channels are strategically positioned to allow for the flow of cool air from the bottom and the expulsion of hot air from the top.
- Heat Accumulation: Natural-air cookstoves often incorporate heat-absorbing materials such as clay, ceramic, or refractory materials. These materials store and release heat gradually, ensuring a consistent and efficient cooking process.
- Insulation: Insulating materials around the combustion chamber help retain heat within the stove, allowing for higher temperatures and improved combustion.

Advantages of Natural-Air Biomass Briquette Cookstoves:
- Simplicity:
- The absence of fans and mechanical components simplifies the design of these stoves, making them easy to use and maintain.
- Users can operate them without the need for external power sources.
- Reduced Emissions:
- Natural convection encourages more complete combustion, resulting in reduced emissions of harmful pollutants and smoke.
- This leads to improved indoor air quality and health benefits for users.
- Low-Cost Operation:
- The lack of electricity-dependent components translates to low operational costs.
- Users don’t need to worry about fan maintenance or power consumption.
- Reliability: These stoves are less prone to mechanical failures, offering greater reliability in areas with limited access to technical support or spare parts.
Forced-air Briquette Cookstoves
- Forced-air briquette cookstoves represent a fusion of ingenuity and sustainability, addressing the critical need for efficient and eco-friendly cooking solutions.
- By marrying forced-air combustion technology with the benefits of biomass briquettes, these stoves offer improved efficiency,
- reduced emissions, and a more user-friendly cooking experience.
- As we navigate the challenges of energy sustainability, forced-air briquette cookstoves stand as a shining example of how innovative thinking can pave the way for a greener and healthier future.
Understanding Forced-Air Briquette Cookstoves:
- At its core, a forced-air briquette cookstove is designed to burn biomass briquettes efficiently by introducing a controlled stream of air into the combustion chamber.
- This forced-air system enhances combustion, resulting in a cleaner, hotter, and more efficient flame.
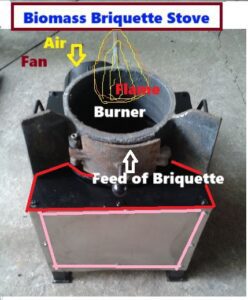
Key Components of Forced-Air Briquette Cookstoves:
- Combustion Chamber: This is where the biomass briquettes are placed and ignited. It’s designed to optimize the burn, ensuring that the briquettes are consumed efficiently.
- Forced-Air Intake: A fan or blower is integrated into the stove to provide a continuous flow of air into the combustion chamber. This forced air not only helps ignite the briquettes but also maintains a steady burn.
- Fuel Hopper: A fuel hopper holds a supply of biomass briquettes, allowing for continuous and controlled feeding into the combustion chamber. This feature reduces the need for constant refilling during cooking.
- Heat Exchanger: In some forced-air cookstoves, a heat exchanger is incorporated to capture and transfer excess heat to a cooking surface, enhancing cooking efficiency.
Advantages of Forced-Air Briquette Cookstoves:
- Efficiency: Forced-air systems ensure that biomass briquettes burn more completely and at higher temperatures, which translates to greater heat output for cooking. This increased efficiency means shorter cooking times and less fuel consumption.
- Reduced Emissions: The controlled combustion in forced-air cookstoves leads to significantly reduced emissions, including harmful smoke and indoor air pollutants. This not only benefits the environment but also the health of users, particularly women and children who are often exposed to indoor air pollution.
- Ease of Ignition: The forced-air system aids in quicker and more reliable ignition of biomass briquettes, making these stoves user-friendly and reducing the time and effort required to start a fire.
- Cooking Consistency: The consistent and high heat output of forced-air briquette cookstoves allows for precise cooking control, making them suitable for a wide range of cooking styles and recipes.
- Fuel Flexibility: These stoves can burn various types of biomass briquettes, providing flexibility based on locally available materials. This versatility ensures that users can adapt to changing fuel sources easily.
Applications of Forced-Air Briquette Cookstoves:
- Household Cooking: These stoves are ideal for household cooking needs, especially in regions where traditional cooking methods are prevalent. They offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative to open fires or basic stoves.
- Institutional Use: Forced-air briquette cookstoves can also be scaled up to serve larger settings such as schools, community centers, and hospitals. They are suitable for cooking meals in bulk efficiently.
- Commercial and Small-Scale Industries: In settings where cooking is an integral part of small-scale industries, such as food processing or catering, these stoves can significantly reduce fuel costs and environmental impact.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
While forced-air briquette cookstoves offer a promising solution for sustainable cooking, several challenges remain:
- Affordability: The initial cost of acquiring a forced-air cookstove may be a barrier for some users. However, long-term fuel savings and health benefits often outweigh this initial investment.
- Maintenance: Like all technology, these stoves require regular maintenance to ensure proper functioning. Training and support for maintenance are essential for users.
- Fuel Supply: The availability of high-quality biomass briquettes is crucial for the efficient operation of these stoves. Ensuring a consistent supply chain can be a challenge in some regions.
Advantages of Biomass Briquette Stoves:
- Environmental Friendliness:
- Perhaps the most significant advantage of biomass briquette stoves is their minimal environmental impact.
- Unlike fossil fuels, burning biomass briquettes releases only the carbon dioxide that the plants absorbed during their growth, resulting in a near-neutral carbon footprint.
- This means that the overall contribution to greenhouse gas emissions is relatively low, which is crucial for combating climate change.
- Waste Utilization:
- Biomass briquette stoves offer a creative solution to the problem of organic waste disposal. Agricultural residues, forest byproducts,
- Household waste is easily converted into valuable briquettes, thereby reducing the burden on landfills and promoting sustainable waste management.
- This dual benefit of waste reduction and energy production is a win-win for the environment.
- Renewable Energy:
- Biomass briquettes are renewable by nature, as they are derived from readily available organic materials.
- This helps reduce our dependency on finite fossil fuel resources and contributes to a more resilient energy infrastructure.
- The sustainability of biomass briquettes makes them a viable long-term energy solution.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Biomass briquette stoves are engineered to optimize combustion, leading to efficient energy conversion.
- The controlled burning process generates a consistent and high heat output, ensuring effective cooking and heating.
- This efficiency translates into reduced fuel consumption, ultimately saving money for users.
- Smoke Reduction:
- Traditional open fires and poorly designed stoves can produce harmful smoke and indoor air pollution.
- Biomass briquette stoves are meticulously engineered to minimize smoke emissions, leading to improved indoor air quality and better health outcomes, particularly for women and children who often spend more time indoors.
- This is a significant public health benefit, particularly in regions where these stoves are commonly used.

Applications of Biomass Briquette Stoves:
Household Cooking:
- In many regions around the world, biomass briquette stoves are the primary choice for cooking purposes.
- Their efficient design and reduced smoke emissions make them a healthier and more sustainable option for households, especially in rural areas where access to cleaner cooking technologies is limited.
- Additionally, these stoves can significantly reduce the time and effort required to collect firewood.
Community Heating:
- Biomass briquette stoves can also be scaled up to serve larger communities or even small industries.
- They provide an economical way to generate heat for various purposes, reducing the demand for fossil fuels and contributing to the local economy.
- This scalability is a testament to their versatility and adaptability.
Emergency Relief:
- In disaster-stricken areas or refugee camps, biomass briquette stoves offer a quick and sustainable solution for cooking and heating.
- They reduce the need to transport and distribute traditional fuels like firewood or kerosene, making them a practical choice for emergency relief efforts.
Challenges and Future Prospects:
While biomass briquette stoves hold immense potential, there are challenges to address to ensure their widespread adoption and success:
Supply Chain of Briquettes
- Ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality biomass briquettes can be challenging in some regions.
- Developing efficient supply chains for raw materials and briquette production is crucial for the sustainability of this technology.
Stove Design:
- Designing stoves that are culturally appropriate and user-friendly is essential for adoption.
- Stove manufacturers and designers need to consider local cooking practices and user preferences to create stoves that are readily accepted and used.
Training and Education
- Proper training on stove operation and maintenance is essential to ensure that users can maximize the benefits of biomass briquette stoves.
- Educational initiatives can help users understand the advantages of these stoves and how to use them effectively.
Government Support:
- Government policies that promote the use of biomass briquette stoves, such as subsidies or incentives, can accelerate their adoption.
- These policies should also address quality standards for briquettes and stoves to ensure safety and performance.
Conclusion
- Biomass briquette stoves stand as a beacon of hope in the quest for sustainable energy solutions.
- By converting organic waste into valuable energy sources, these stoves offer a cleaner, greener, and more equitable way to cook and heat our homes.
- As we continue to prioritize environmental responsibility and energy efficiency, biomass briquette stoves are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping a brighter and more sustainable future for generations to come.
- Their advantages in terms of environmental impact, waste utilization, renewable energy, efficiency, and smoke reduction make them a compelling choice for a world in need of sustainable solutions.
References
- Briquette Stoves in rural areas in South Africa
- Jwala In India, Biomass stoves
