Scope of Charocal Briquette
What is charcoal briquette?
- Charcoal briquettes are primarily composed of charcoal, which is obtained by burning wood in a low-oxygen environment, often referred to as the pyrolysis process. Other ingredients can include coal dust, sodium nitrate, sawdust, and other binders or accelerants.
- Charcoal briquettes are a popular fuel source for barbecues and grills. They are typically made from a combination of charcoal, coal, starch (as a binder), and sometimes other additives.

Heating Value
- The heating value of charcoal briquettes can vary based on various factors, including their composition, manufacturing process, and quality. However, in general, charcoal briquettes have a high heating value.
- They typically have a calorific value of around 7,000-8,000 BTUs per ounce or 25-35 megajoules per kilogram.
- This high heating value is what makes charcoal briquettes a popular choice for grilling and barbecuing. They burn at high temperatures, providing a consistent and even heat source, which is essential for cooking food on a grill.
- The heat output and duration of burning can be influenced not only by the quality of the briquettes but also by the ventilation in the grill, the quantity of briquettes used, and the method of lighting and maintaining the firing
Advantages of Charcoal Briquettes
- Charcoal briquettes offer several advantages over other types of briquettes, such as coal briquettes or wood briquettes, which contribute to their popularity in various applications.
- Here are some of the benefits of charcoal briquettes:
Cleaner Burning
- Charcoal briquettes produce less smoke and fewer harmful emissions compared to lump charcoal or coal or wood briquettes.
- This makes them a more environmentally friendly and healthier choice, particularly for indoor cooking or heating.
- The process of making smokeless charcoal is presented in the post.

High Heat Output:
- Charcoal briquettes have a high energy density and can produce intense heat, making them ideal for grilling, barbecuing, and other high-heat applications.
- They ignite quickly and reach a high temperature, allowing for efficient cooking.
Consistency:
- Charcoal briquettes are uniform in size and composition, which results in consistent burning.
- This predictability is crucial for cooking and grilling, as it helps maintain an even temperature and cooking performance.
Long Burning Time:
- Charcoal briquettes typically have a longer burning time compared to wood briquettes or raw wood.
- This means fewer refueling or reloading intervals when using charcoal briquettes.
Lower Moisture Content:
- Charcoal briquettes have a low moisture content, which means they ignite more easily and are less prone to extinguishing during use.
- This quality is particularly advantageous for grilling and cooking.
Reduced Ash Production:
- charcoal briquettes produce less ash residue compared to wood briquettes.
- This results in easier and less frequent cleaning of grills or stoves.
Versatility:
- Charcoal briquettes are suitable for a wide range of applications, from outdoor grilling to cooking and heating in various settings.
- They are often used in portable grills, making them a convenient choice for picnics and outdoor events.
Uniform Shape and Size:
- Charcoal briquettes are typically produced in uniform shapes and sizes, making them stackable and easy to store in bags or containers.
- This makes them more convenient for consumers.
Conservation of Natural Resources:
- Charcoal briquettes reduce the demand for wood and coal, helping to conserve natural resources and reduce deforestation.
Availability:
- Charcoal briquettes are widely available in most regions, making them easily accessible to consumers for various purposes.
While charcoal briquettes offer these advantages, it’s essential to consider the specific needs and applications when choosing between different types of briquettes. The choice may also depend on factors like availability, cost, and environmental considerations.

How to Produce Charocal Briquette
- Producing charcoal briquettes involves a process that transforms biomass material into a compact, high-density, and efficient fuel source.
- Here’s a general guide on how to produce charcoal briquettes:
Materials and Equipment Required:
- Biomass Material: Commonly used materials include sawdust, agricultural residues (such as rice husks or straw), coconut shells, or other organic waste.
- Binder: This helps hold the briquettes together. Binders can be starch, molasses, or other adhesive materials.
- Briquette Press or Extruder: Machines designed to compress the biomass material into briquettes.
- Drying Equipment: A drying system to reduce the moisture content of the briquettes.
- Carbonization Equipment (Optional): For converting the briquettes into charcoal through a carbonization process.
Major Process:
- Material Preparation:
- Dry the biomass material if it’s not already dry to reduce its moisture content.
- Moisture content should ideally be below 12% for effective briquette production.
- Chop or crush the material into smaller pieces. Sawdust works well due to its fine texture.
- Mixing:
- Mix the dried biomass material with the binder.
- The ratio depends on the material used, but typically it ranges from 3:1 to 8:1 biomass to binder.
- Briquette Formation:
- Feed the mixed material into the briquette press or extruder.
- The machine will compress the material under high pressure, forming it into the desired briquette shape. The pressure and mold used will affect the density and shape of the briquette.
- Drying:
- The formed briquettes need to be dried to reduce their moisture content further.
- Use a drying system (could be sunlight, an oven, or a dedicated drying chamber) until the moisture content is low enough for efficient burning.
- Carbonization (Optional for Charcoal):
- If your goal is to produce charcoal briquettes, a separate carbonization process is required.
- Place the dried briquettes in a kiln or retort designed for carbonization.
- Heat the briquettes at a high temperature (300-500°C) in a low-oxygen environment. This drives off volatile compounds and leaves behind the carbonized briquettes, converting them into charcoal.
- Cooling and Packaging:
- Once carbonization is complete, let the charcoal briquettes cool down.
- Package the finished briquettes for storage or sale.
Tips:
- Experiment with ratios: The ratio of biomass to binder can vary depending on the material and desired briquette properties.
- Quality control: Ensure the briquettes are of good quality and consistency for efficient burning.
- Safety: Follow safety protocols, especially during the carbonization process, which involves high temperatures.
- The process can vary in complexity and scale, but this basic process can be adapted according to the available materials and equipment given in the post. Commercial production might involve more advanced machinery and processes for higher efficiency and quality control.

Types and Size Charcoal briquette
- Charcoal briquettes come in various types and sizes, catering to different applications and preferences.
- The choice of type and size depends on how and where you plan to use them. Here are some common types and sizes of charcoal briquettes:
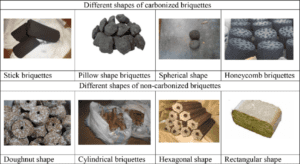
Types of Charcoal Briquettes:
- Standard Charcoal Briquettes:
- These are the most common charcoal briquettes found in most stores.
- They are typically made from a mixture of charcoal dust, binders, and sometimes other additives.
- Standard briquettes are known for their consistent size, long burning time, and relatively low ash production.
- Lump Charcoal Briquettes:
- Lump charcoal briquettes are made from pure hardwood and have no binders or additives.
- They are considered a more natural and cleaner-burning option. Lump briquettes are known for their high heat output and faster ignition.
- They can be irregularly shaped compared to standard briquettes.
- Instant Lighting Charcoal Briquettes:
- These briquettes come with a built-in ignition system, such as lighter fluid-infused briquettes.
- They are convenient for quick and easy grilling or cooking because they ignite with minimal effort. However, some people may find them to have a chemical taste.
- Flavored Charcoal Briquettes:
- These briquettes are infused with various flavors to add a smoky or seasoned taste to grilled food.
- Common flavors include hickory, mesquite, and applewood. Flavored briquettes can enhance the flavor of your dishes.
Barbecue Charcoal Briquettes (BCB)
- Barbecue Charcoal Briquettes (BCB) are compact blocks of charcoal used for grilling, smoking, and barbecuing.
- They are made by compressing charcoal, typically made from wood byproducts or sawdust, along with binding agents, into uniform shapes. These briquettes are popular among grilling enthusiasts due to their consistent burning and heat production.
Here’s a basic overview of barbecue charcoal briquettes:
Manufacturing of BCB
- The process involves charring wood or other organic materials in the absence of oxygen, which creates charcoal.
- The charcoal is then crushed into small pieces, mixed with binders, and shaped into uniform briquettes under pressure.
Advantages of BCB
- Uniform Burning: Briquettes generally burn more consistently and for a longer duration than natural lump charcoal.
- Steady Heat: They tend to maintain a steady temperature, which makes them suitable for prolonged grilling sessions.
- Easy to Use: Charcoal briquettes are relatively easy to light and offer a convenient grilling experience.
- Less Smoke: They produce less smoke compared to traditional wood, allowing for a more controlled grilling environment.
Considerations in the Production of Briquette
- Additives:
- Some charcoal briquettes may contain additives or chemicals used as binders.
- Check the product details if you have specific preferences or concerns about additives.
- Burn Time:
- While they burn longer, they may take a bit longer to reach the desired cooking temperature compared to natural lump charcoal.
- Ash Production:
- Briquettes tend to produce more ash than lump charcoal, which might require occasional clearing during long grilling sessions.
Use of Charcoal Briquettes
- Lighting: Use a chimney starter or lighter cubes to ignite the briquettes. Avoid using lighter fluid if possible to prevent any chemical taste in the food.
- Distribution: Spread the briquettes evenly in your grill for consistent heat across the cooking surface.
- Grilling: Wait until the briquettes are covered with a light gray ash before cooking. This ensures they’re properly heated and ready for grilling.
Always follow safety guidelines and the manufacturer’s instructions when using charcoal briquettes to ensure safe and efficient grilling.
- Remember, there are various brands and types of charcoal briquettes available, each with its own specific qualities, so you can explore different options to find the one that suits your grilling needs the best.

Sizes of Charcoal Briquettes:
- Standard Size: The typical size for most charcoal briquettes is about 2 inches (5 cm) in diameter and 1 inch (2.5 cm) in thickness. This size is suitable for most grilling and barbecue applications.
- Mini Briquettes: Smaller briquettes, often about half the size of standard briquettes, are available for portable grills and small cooking setups. They can be convenient for compact grills or quick cooking needs.
- Large Briquettes: Some manufacturers produce larger briquettes for use in large grills or smokers. These larger briquettes can provide a longer burning time, making them ideal for slow and low-temperature cooking methods like smoking.
- Oval or Pillow-Shaped Briquettes: These briquettes have a unique shape, often with a slight oval or pillow-like form. They may be designed for specific grilling or cooking equipment.
Charcoal Burners
- Charcoal briquette can be used for burners for cooking which has the following features
-
Hookah Coal Burner
-
Fire Charcoal Lighter, Hot Plate for Cooking
-
Coal Charge
-
Powder Coated Metal Coal Stove
-
Cost of charcoal briquettes
The cost of charcoal briquettes can vary significantly based on various factors, including the region, raw materials used, production scale, quality, and market demand. Here are some factors that influence the cost of charcoal briquettes:
- Raw Materials:
-
- The cost of the primary raw material, which is typically charcoal dust or biomass, can vary depending on its availability and quality.
- For example, charcoal dust might be cheaper than certain types of biomass.
- The cost of binders also factors into the overall cost.
-
- Production Scale:
- Smaller-scale producers may have higher production costs per unit compared to larger manufacturers who benefit from economies of scale.
- Small-scale producers might need to manually handle more aspects of production, such as mixing and forming the briquettes, which can increase labor costs.
- Labor Costs:
- Labor costs can significantly affect the overall cost of production.
- Skilled labor and machinery operation might require higher wages, especially in developed countries, compared to regions with lower labor costs.
- Equipment Costs:
- The cost of the briquette press or extruder and any additional equipment used in the production process can vary widely.
- High-quality, automated equipment tends to be more expensive but can improve efficiency and product quality.
- Transportation Costs:
- The cost of transporting raw materials and finished briquettes to and from production facilities can influence the final cost.
- Proximity to raw materials and markets can help lower transportation costs.
- Quality Control:
- Ensuring consistent quality of charcoal briquettes may require quality control measures, which can add to the overall cost.
- Market Demand:
- In regions where there is high demand for charcoal briquettes, prices may be higher due to increased competition.
- Conversely, in areas with limited demand, prices might be lower.
- Environmental Regulations:
- Compliance with environmental regulations can result in additional costs, particularly if production methods need to meet specific standards.
- Packaging:
- The cost of packaging materials, branding, and labeling can affect the final retail price of charcoal briquettes.
- It’s important to note that the cost of charcoal briquettes can vary widely from one location to another.
- In many regions, charcoal briquettes are an affordable and cost-effective alternative to traditional charcoal or firewood, making them an attractive option for households and businesses.
- To get the most accurate and up-to-date information on the cost of charcoal briquettes, you may want to contact local producers, suppliers, or retailers in your area.
Briquette Costs In India
- The cost of charcoal briquette is around Rs 300 for 50 tablets
- One kg of charcoal costs around Rs 5-10 if packing and transportation cost is excluded
Summary
- The choice of charcoal briquette type and size largely depends on personal preference and the cooking equipment you use.
- Different types and sizes of briquettes can offer various benefits in terms of flavor, heat output, and convenience, so you can select the one that best suits your needs.
- Additionally, it’s essential to consider the quality and composition of the briquettes to ensure they meet your specific requirements.
References
- Charcoal Briquette Biomass Manufactures, FTM Machinery
- Charcoal Briquette Plant, Machinery and Processes
- Advantages of barbeque coal briquette over lump charcoal, Serious Eat site
