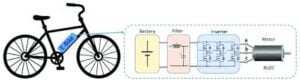
Major parts of the E cycle
- An electric cycle, also known as an e-bike, combines traditional pedal power with electric propulsion. Here’s a breakdown of its working principle:
- Battery: The heart of an electric cycle, typically a lithium-ion battery, provides the electrical energy required to power the motor. The battery is rechargeable and can be charged using a standard electrical outlet.
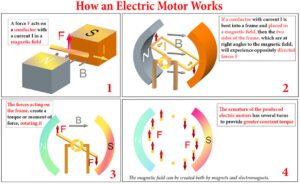
- Motor: The motor is the component that converts electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to drive the bike. There are two main types of motors:
- Hub Motor: Located in the wheel hub (front or rear), it directly drives the wheel.
- Mid-Drive Motor: Located near the bike’s crank, it provides power to the bike’s chain, assisting the rider’s pedaling.
- Controller: The controller regulates the power output from the battery to the motor. It ensures smooth power delivery based on the rider’s input and selected mode of assistance.
- Pedal Assist System (PAS): This system uses sensors (such as torque or cadence sensors) to detect the rider’s pedaling. The controller adjusts the motor’s power output based on the detected pedaling effort, providing a seamless boost to the rider’s input.
- Throttle (optional): Some e-bikes have a throttle, which allows the rider to engage the motor directly without pedaling. This is similar to how a scooter operates.
- Display Panel: Most e-bikes come with a display panel that shows battery level, speed, distance traveled, and other important metrics. It also allows the rider to select different levels of pedal assistance.
Life Expectancy of an Electric Cycle
- The lifespan of an electric cycle depends on various factors, including the quality of components, usage, and maintenance. Here’s a general overview:
- Battery Life:
- Average Lifespan: Typically 3-5 years or 500-1000 charge cycles.
- Factors Affecting Life: Frequency of charging, depth of discharge, and storage conditions. Proper care, such as avoiding deep discharges and storing in a cool, dry place, can extend battery life.
- Motor Life:
- Average Lifespan: 5-10 years or more, depending on usage.
- Factors Affecting Life: Regular maintenance, avoiding overloading, and proper use.
- Other Components:
- Frame: Can last many years with proper care, typically over 10 years.
- Brakes, Tires, and Chains: These wear out faster and need regular replacement. Brakes and tires may need replacement every 1-2 years, while chains can last 2-3 years depending on usage.

Electric Cycles in India
Scope Electric Cycles in India
- The market for electric cycles in India is growing rapidly seen in the news,
- Its demand is driven by increasing environmental awareness, rising fuel costs, and the need for sustainable urban mobility solutions.
- Here’s an overview of the electric cycle landscape in India:

Popular Electric Cycle Brands in India
- Hero Lectro
- Models: Hero Lectro C1, Hero Lectro F1, Hero Lectro EHX20, etc.
- Features: Lightweight, various range options, pedal assist, and throttle modes.
- Target Audience: Urban commuters, fitness enthusiasts, and recreational riders.
- Nexzu Mobility
- Models: Nexzu Roadlark, Nexzu Dextro, Nexzu Bazinga.
- Features: Long-range, removable batteries, stylish designs.
- Target Audience: Commuters, long-distance riders.
- Ampere
- Models: Ampere Magnus, Ampere Reo.
- Features: Affordable pricing, decent range, reliable performance.
- Target Audience: Budget-conscious riders, daily commuters.
- Firefox
- Models: Firefox Adventron, Firefox Bad Attitude.
- Features: High-quality components, off-road capabilities.
- Target Audience: Adventure cyclists, off-road enthusiasts.
- EMotorad
- Models: EMX, T-Rex, Doodle.
- Features: High-performance motors, long-range batteries, sturdy build.
- Target Audience: Fitness enthusiasts, adventure riders.
- Stryder
- Models: Stryder Zeeta, Stryder Zeeta Plus.
- Features: Lightweight frames, good battery life, comfortable ride.
- Target Audience: Urban commuters, casual riders.

Best e-cycle in India
Advantages of Electric Cycles in India
- Cost Savings:
- Low Operating Costs: Compared to petrol or diesel vehicles, electric cycles have significantly lower running costs.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Government incentives and subsidies for electric vehicles can reduce the initial purchase cost.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Zero Emissions: Electric cycles do not emit pollutants, helping reduce air pollution in cities.
- Sustainable Transportation: Promotes a green mode of transport, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Health and Fitness:
- Physical Activity: Encourages regular exercise with the option of pedal assistance.
- Mental Well-being: Cycling can improve mental health by reducing stress and promoting outdoor activity.
- Traffic and Parking:
- Reduced Congestion: E-bikes can help alleviate traffic congestion in urban areas.
- Easy Parking: They require less parking space compared to cars.
- Convenience and Flexibility:
- Last-Mile Connectivity: Ideal for short commutes and bridging gaps in public transport.
- Variety of Models: Available in various designs and specifications to cater to different needs.
Challenges and Considerations
- Infrastructure:
- Lack of Dedicated Lanes: Limited cycling lanes in many Indian cities can make riding less safe.
- Charging Facilities: Insufficient charging infrastructure for electric cycles.
- Initial Cost:
- Higher Upfront Cost: Electric cycles can be more expensive upfront compared to traditional bicycles.
- Battery Life and Range:
- Limited Range: The range of electric cycles is typically between 30-100 km, which may not be sufficient for longer commutes.
- Battery Replacement: Batteries need to be replaced after a few years, adding to long-term costs.
- Awareness and Adoption:
- Consumer Awareness: There is still a need to increase awareness about the benefits of electric cycles.
- Adoption Rate: Adoption may be slow due to cultural preferences for motorbikes and cars.
Future Outlook
The future of electric cycles in India looks promising with the potential for widespread adoption. Key factors driving this growth include:
- Government Support: Policies promoting electric vehicles, subsidies, and investment in infrastructure.
- Technological Advancements: Improvements in battery technology, motor efficiency, and smart features.
- Urbanization: Increasing urbanization and the need for efficient and sustainable transportation options.
- Health and Environment: Growing awareness of health and environmental benefits.
With these factors in play, electric cycles are set to become a significant mode of transport in India’s urban landscape, contributing to a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable future.
Maintenance Tips
- Battery: Charge regularly, avoid full discharges, and store in a cool place.
- Motor: Regularly check for any unusual noises or issues and have it serviced if needed.
- General: Regularly clean the bike, check tire pressure, and ensure brakes and gears are functioning properly.
- By following proper maintenance and usage guidelines, you can ensure that your electric cycle remains in good condition for many years.