What is rainwater harvesting?
- Rainwater harvesting is the process of collecting, storing, and utilizing rainwater for various purposes. It involves capturing rainwater that falls on surfaces like rooftops, land, or paved areas, and directing it into storage systems for later use.
- The collected rainwater can be used for both non-potable (non-drinking) and potable (drinking) purposes, depending on the level of treatment it undergoes.
- Some common uses of harvested rainwater include irrigation, toilet flushing, laundry, landscape watering, livestock watering, and even drinking water after appropriate treatment.
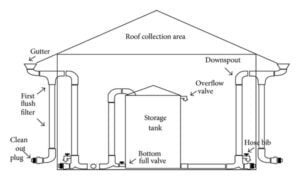
Parts of Rainwater Harvesting Systems (RWHS)
Rainwater harvesting systems typically consist of the following components:
Catchment Surface:
- This is the surface area on which rainwater falls and is collected. It can be the rooftops of buildings, paved areas, or even land surfaces.
Gutters and Downspouts
- These are used to collect rainwater from rooftops and direct it into a storage system.
- Gutters are usually installed along the edges of the roof, and downspouts carry the water from the gutters to the storage tanks or reservoirs.
Filtration System:
- Rainwater may contain debris, leaves, and other pollutants.
- A filtration system is used to remove these impurities before the water enters the storage system. It ensures that the harvested water is clean and suitable for the intended purpose.
Storage Tanks or Reservoirs:
- Rainwater is stored in tanks or reservoirs for later use.
- These storage systems can be above-ground or underground, depending on available space and aesthetic considerations. They are typically equipped with appropriate covers to prevent contamination and mosquito breeding.
Distribution System:
- A distribution system is used to convey the harvested rainwater to the desired points of use.
- It can include pipes, pumps, and controls to regulate the flow and pressure of the water.
Treatment System (optional):
- If the harvested rainwater is intended for potable use, additional treatment processes such as filtration, disinfection, and purification may be required to meet drinking water standards.
- Rainwater harvesting offers numerous benefits, including reducing the demand for freshwater sources, mitigating stormwater runoff and flooding, improving water security, and promoting sustainable water management practices.
- It is an environmentally friendly and cost-effective approach to water conservation and can be implemented on various scales, from individual homes to large commercial buildings and community-level systems.
Types of Rainwater harvesting technique
Rainwater harvesting techniques are methods used to collect, store, and utilize rainwater for various purposes. Here are some common techniques:
Roof-Based Rainwater Harvesting
- This technique involves collecting rainwater that falls on rooftops.
- The water is directed to gutters and downspouts, which lead to storage tanks or reservoirs.
- The collected water can be used for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and laundry.

Surface Runoff Harvesting
- In areas with sloping terrain, surface runoff harvesting is used to capture rainwater from paved surfaces or open ground.
- Channels or trenches are constructed to divert the runoff water into storage tanks, ponds, or recharge pits.
Rainwater Harvesting Ponds:
- Artificial ponds or tanks are constructed to capture rainwater.
- These structures are designed to maximize water storage capacity and minimize evaporation.
- The collected water can be used for irrigation, groundwater recharge, or as a source of drinking water after treatment.
Underground Storage Systems:
- Underground storage systems involve the installation of storage tanks or cisterns beneath the ground to collect rainwater. These systems are suitable for areas where above-ground space is limited or aesthetic considerations are important.
- The collected water can be used for a wide range of purposes.
Percolation Pits and Recharge Wells:
- Percolation pits or recharge wells are used to recharge groundwater aquifers by allowing rainwater to percolate into the soil.
- These techniques are beneficial in areas facing groundwater depletion.
- The pits or wells are typically filled with coarse gravel or porous materials to facilitate water infiltration.
Check Dams:
- Check dams are small structures constructed across seasonal streams or gullies to slow down the flow of water and create small reservoirs.
- They help in conserving rainwater by allowing it to seep into the ground and recharge the surrounding soil and groundwater.
Fog Harvesting:
- In arid regions or fog-prone areas, fog harvesting techniques are employed.
- Mesh or netting structures are set up to capture tiny water droplets from fog, which then accumulate and drip into collection systems. This method can provide a supplemental water source in regions with low rainfall.
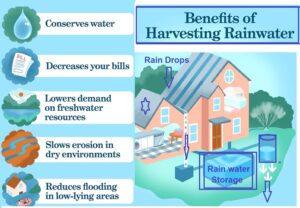
Benefits of Rainwater harvesting
Rainwater harvesting offers several benefits, both for individuals and communities, as well as for the environment. Here are some key advantages of rainwater harvesting:
Water Conservation
-
- Rainwater harvesting helps conserve water by capturing and utilizing rainfall that would otherwise be lost as runoff.
- It reduces the strain on freshwater sources such as rivers, lakes, and underground aquifers, especially in areas facing water scarcity or drought conditions.
Sustainable Water Supply:
- Harvested rainwater can serve as an additional or alternative water supply for various purposes.
- It can be used for non-potable uses like irrigation, toilet flushing, laundry, and cleaning, reducing the reliance on treated drinking water for such activities.
Cost Savings:
- Utilizing harvested rainwater can lead to cost savings in water bills, particularly for activities that do not require treated water.
- Depending on the local water rates, rainwater harvesting systems can provide significant long-term financial benefits for homeowners, businesses, and institutions.
Flood and Erosion Control:
- By capturing rainwater and directing it into storage systems, rainwater harvesting reduces stormwater runoff.
- This helps in mitigating flooding, erosion, and the pollution of water bodies caused by excessive runoff carrying pollutants from impervious surfaces.
Groundwater Recharge
- Rainwater harvesting techniques like percolation pits and recharge wells facilitate the replenishment of groundwater aquifers.
- They allow rainwater to infiltrate into the ground, restoring underground water levels and promoting the sustainability of water resources.
Environmental Benefits
- Rainwater harvesting has several environmental advantages.
- It reduces the demand for energy-intensive water treatment and distribution processes, conserves ecosystems by reducing the extraction of water from natural sources, and decreases the carbon footprint associated with water consumption.
Resilience to Climate Change
- As climate change brings about more frequent and intense rainfall events, rainwater harvesting systems can help capture excess rainwater, preventing flooding and reducing strain on stormwater drainage systems. It contributes to building resilience in the face of changing weather patterns.
Educational and Community Engagement:
- Implementing rainwater harvesting systems provides opportunities for education and community involvement. It raises awareness about water conservation, fosters a sense of responsibility towards the environment, and promotes sustainable practices among individuals and communities.
Cost of Rainwater Harvesting
- In India, the cost of a water harvesting system could vary from Rs 1,500 to 25,000 for buildings of about 300 square meter home.
- The cost depends on the quality and quantity of materials like collecting pipes, ducts, sediment and filtration, and water tanks
- Example: Delhi has planned a rainwater harvesting system for each home cost varies from Rs 50,000 (USD 10000) to Rs 1.5 lakh (USD 20,000) for societies, hospitals.
- The cost of rainwater harvesting systems can vary depending on various factors such as the size of the system, the complexity of the installation, the materials used, and the region where it is being implemented. Here are some general cost considerations for rainwater harvesting:
- Collection System:
- The cost of the collection system primarily depends on the size of the catchment area (e.g., roof size), the material used for the gutters and downspouts, and the number and size of storage tanks.
- Basic collection systems can range from a few hundred dollars for smaller setups to several thousand dollars for larger, more sophisticated systems.
- Storage Tanks:
- Common materials include plastic, fiberglass, concrete, or steel.
- The cost of storage tanks depends on their material, capacity, and quality.
- Prefer high-quality Plastic tanks for easier installation. As concrete and steel tanks are generally more heavy and expensive
- The cost per liter of plastic tank storage is Rs 5 to 10 in India.
- The cost of storage tanks can range from a few hundred dollars for smaller plastic tanks to several thousand dollars for larger or higher-quality tanks.
- Filtration and Treatment
- Depending on the intended use of the harvested rainwater, filtration, and treatment systems may be necessary.
- Some water Filtration systems can remove debris and sediment, while treatment systems can address water quality concerns.
- The cost of these systems varies widely based on their complexity and capacity.
- Simple filters can range from Rs 3500 ( $50) to a few hundred dollars, while comprehensive treatment systems can cost several thousand dollars.
- Installation and Labor:
- The cost of installation can vary depending on the complexity of the system and the labor rates in your area.
- If you hire professionals for installation, labor costs can add significantly to the overall expenses.
- However, some rainwater harvesting systems can be installed by homeowners, which can help save on labor costs.
- Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance is important to keep the rainwater harvesting system functioning optimally. This may include cleaning gutters, inspecting tanks for leaks, checking filters, and performing any necessary repairs. The cost of maintenance will depend on the complexity of the system and whether you hire professionals or do it yourself.
Summary
- It’s important to note that the benefits of rainwater harvesting can vary depending on factors such as climate, geographic location, water demand, and the specific techniques used.
- Proper design, maintenance, and adherence to local regulations are essential to ensure the effectiveness and sustainability of rainwater harvesting systems.
- It’s worth noting that the suitability and effectiveness of these techniques can vary depending on factors such as climate, geography, water demand, and available resources.
- Local regulations and guidelines should be followed when implementing rainwater harvesting systems to ensure sustainability and environmental compatibility
- It’s important to note that the cost estimates provided here are general and can vary significantly based on factors such as the location, system requirements, and specific components chosen.
- It is advisable to obtain quotes from suppliers and contractors in your area to get a more accurate estimate for your particular rainwater harvesting project