Table of Contents
ToggleTechniques of Waste Water Treatment
- Recycling wastewater at home can significantly reduce water consumption and lower utility bills.
- Here are some effective techniques for wastewater recycling in a home setting:
Greywater Recycling Systems
- What it is: Greywater refers to gently used water from sinks, showers, bathtubs, and washing machines (excluding toilets).
- How it works: This water can be treated and reused for non-potable purposes, such as toilet flushing, irrigation, and cleaning.
- Components: A basic greywater system includes a collection tank, filters, pumps, and a distribution system.
- Benefits: Reduces water waste and lowers demand on fresh water resources.
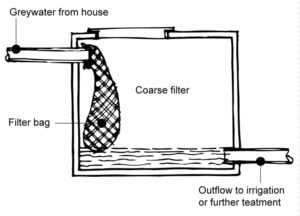
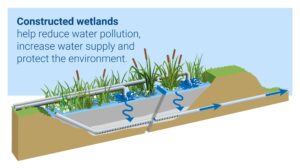
Constructed Wetlands
- What it is: A natural system that uses plants, soil, and microorganisms to filter and treat greywater.
- How it works: Greywater is channeled into a constructed wetland where it passes through a series of plants and soil layers, which naturally filter contaminants.
- Applications: Suitable for garden irrigation after treatment.
- Benefits: Low-maintenance, eco-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing.
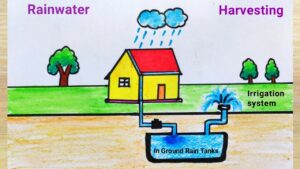
Rainwater Harvesting Systems
- What it is: Collecting and storing rainwater for future use.
- How it works: Rainwater is collected from rooftops, filtered, and stored in tanks. It can be used directly or combined with greywater systems.
- Applications: Ideal for irrigation, toilet flushing, and even laundry.
- Benefits: Reduces reliance on municipal water supply and can be integrated with other recycling systems.
Reed Bed Systems
- What it is: Similar to constructed wetlands, reed beds use reeds and other aquatic plants to filter and clean greywater.
- How it works: Wastewater flows through a bed of reeds where natural processes break down pollutants.
- Applications: Typically used for treating greywater for irrigation.
- Benefits: Natural, low-energy, and effective in reducing wastewater.
Advanced Filtration Systems
- What it is: Uses mechanical, biological, and chemical processes to treat wastewater.
- How it works: Water passes through multiple stages of filtration, including sand filters, activated carbon filters, and sometimes UV disinfection.
- Applications: Suitable for more comprehensive water recycling, including potable water reuse in some cases.
- Benefits: High level of treatment, making water safe for a variety of uses.
Membrane Bioreactors (MBRs)
- What it is: A combination of biological treatment and membrane filtration.
- How it works: Wastewater is treated biologically, and then passed through membranes that filter out remaining solids and microorganisms.
- Applications: Can be used for greywater and blackwater (toilet water) treatment.
- Benefits: Produces high-quality treated water, suitable for various non-potable uses.
Composting Toilets
- What it is: Toilets that treat human waste through composting, reducing water use and creating usable compost.
- How it works: Waste is separated, dried, and composted over time, transforming it into a safe fertilizer.
- Applications: Best for areas with limited water resources or as part of an eco-friendly home design.
- Benefits: Eliminates water use for flushing, reduces waste, and produces valuable compost.

Drip Irrigation Systems
- What it is: An efficient irrigation method that delivers water directly to the roots of plants.
- How it works: Treated greywater is distributed through a network of tubes with small emitters, minimizing water loss.
- Applications: Ideal for garden irrigation.
- Benefits: Reduces water waste, promotes healthy plant growth, and is compatible with greywater systems
UV Purification
- UV light can be used to disinfect water by killing bacteria and other pathogens.
- It’s often used in greywater recycling systems as a final treatment step before the water is reused.
Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS)
- Though primarily used in fish farming, RAS technology can be adapted for home use, where water from fish tanks is filtered and recirculated.
- The filtered water, rich in nutrients, can be used for hydroponic gardening.
Summary
- By implementing these techniques, homeowners can significantly reduce water usage, lower utility bills, and contribute to environmental sustainability.
- these techniques requires considering the specific needs of your household, local regulations, and the initial costs of setup. However, they can significantly reduce water usage and promote sustainable living.
Post Views: 636
