Table of Contents
ToggleModern Biomass Stoves
- Modern smokeless biomass cooking methods aim to reduce the harmful smoke and pollutants associated with traditional biomass cooking.
- Biomass energy is poised to play a significant role in the future energy landscape due to its renewable nature and potential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Refer are some key aspects of biomass energy and its prospects for the future
- Sustainability and Renewability” Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as plant matter, agricultural residues, and organic waste.
- Best Biomass Stoves in the Market with Cleaner Cooking
Improved Biomass Cookstoves
Improved biomass cookstoves are designed to maximize combustion efficiency and minimize smoke production. These stoves often incorporate features such as insulated combustion chambers, chimneys, and air vents to enhance airflow and combustion.
- Key Features:
- Insulated combustion chambers
- Chimneys for venting smoke
- Airflow control mechanisms
- Benefits: Reduced smoke emissions, improved fuel efficiency, and better health outcomes due to decreased indoor air pollution.
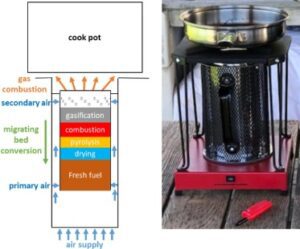
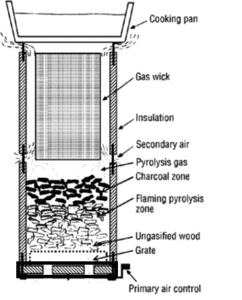
Gasifier Stoves
Gasifier stoves operate by converting biomass into a combustible gas through a process called gasification. This gas is then burned, resulting in a cleaner and more efficient cooking process.
- Key Features:
- Two-stage combustion process
- High-temperature combustion
- Benefits: Very low smoke emissions, high thermal efficiency, and the ability to use various types of biomass such as wood chips, pellets, and agricultural residues.
Pellet Stoves
Pellet stoves use compressed biomass pellets made from wood waste, agricultural residues, or other organic materials. These stoves are designed to burn pellets efficiently with minimal smoke.
- Key Features:
- Automated fuel feeding systems
- Controlled combustion
- Benefits: Consistent and clean burning, reduced smoke and ash production, and higher efficiency compared to traditional biomass stoves.
- Refer to the article of Biomass Briquette or wooden Pellet which is better for cooking

Biogas Stoves
Biogas stoves utilize biogas produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter such as animal manure, kitchen waste, and agricultural residues.
- Key Features:
- Use of biogas as a clean fuel
- Simple and safe operation
- Benefits: Smokeless combustion, renewable fuel source, and reduced reliance on traditional biomass.

Ethanol Stoves
Ethanol stoves burn ethanol, a clean liquid fuel derived from biomass. These stoves are designed to provide a smoke-free cooking experience.
- Key Features:
- Use of liquid ethanol fuel
- Clean combustion
- Benefits: No smoke or soot, ease of use, and renewable fuel source.

Solar-Biomass Hybrid Stoves
These stoves combine solar energy with biomass to reduce smoke emissions and improve efficiency. They use solar energy when available and switch to biomass fuel when needed.
- Key Features:
- Solar energy integration
- Backup biomass combustion
- Benefits: Reduced biomass consumption, lower smoke emissions, and enhanced sustainability.

Forced Draft Stoves
Forced draft stoves use small, battery-operated fans to improve airflow and combustion efficiency. This results in more complete burning of the biomass and significantly less smoke.
- Key Features:
- Battery-operated fans
- Enhanced airflow control
- Benefits: Dramatically reduced smoke emissions, increased fuel efficiency, and improved cooking speed.

Conclusion
- Modern smokeless biomass cooking methods leverage advanced technologies to provide cleaner, more efficient, and healthier cooking solutions.
- By reducing smoke emissions, these methods not only improve indoor air quality but also contribute to better health outcomes and environmental sustainability.
