Kitchen Chimney Design Guidelines in India
Installation Height
-
Ideal mounting height above cooktop:
-
Gas stove: 60 to 75 cm (24 to 30 inches)
-
Electric/Induction: 45 to 60 cm
-
-
Lower than this risks fire; higher reduces suction efficiency.
Suction Power Guidelines
-
Measured in m³/hr. Indian kitchens usually require high suction due to spices and frying.
| Cooking Style | Suggested Suction Power |
|---|---|
| Basic boiling/steaming | 400–600 m³/hr |
| Regular frying/spices | 700–1000+ m³/hr |
| Open/congested kitchen | 1000–1200 m³/hr |
Filter Type (Choose Wisely)
| Filter Type | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Baffle | Indian kitchens | Metal filters redirect airflow, easy to clean |
| Mesh | Light cooking | Gets clogged faster, needs frequent cleaning |
| Filterless | Modern option | Uses centrifugal force, low maintenance |
Ducting Standards
-
Material: Rigid stainless steel or aluminum (not plastic or flexible PVC)
-
Diameter: Minimum 6 inches (150 mm), better if 8 inches for high-power chimneys
-
Length: Keep under 10 feet (3 meters) if possible
-
Bends: Max of 2–3 bends, use wide radius elbows
Duct Design Guidelines
-
Material: Stainless steel or rigid PVC preferred
-
Diameter: Minimum 6 inches (150 mm)
-
Length: As short and straight as possible (≤ 10 feet ideal)
-
Elbows/Bends: Max 2–3 gentle bends (avoid sharp 90° turns)
-
Exhaust Outlet: Should exit to open air, not into attic/loft

Suction volume of chimney in kitchen
Electrical Setup & Power
-
Install socket about 1 foot above chimney height
-
Keep wiring enclosed in PVC conduit for safety
- Chimney should have a dedicated 10A or 15A electrical connection.
-
Socket ideally placed 6–12 inches above chimney height.
-
All equipment should be earthed and protected by an MCB.
Ease of Cleaning & Maintenance
-
Plan for easy filter access and monthly cleaning
-
Some models come with auto-clean features (good for oily cooking)
-
Ensure oil collection trays are accessible
Wall & Mount Considerations
-
Best on external wall to minimize ducting
-
Avoid placing under open windows or cabinet obstructions
-
Ensure solid anchoring to hold chimney weight (~10–15 kg)
Ventilation and Draft Control
-
Use a back-draft damper in the duct to prevent outside air or insects entering
-
Vent termination should have a rain cap or cowl to prevent water ingress
Compliance & Best Practices
-
Refer to National Building Code (NBC) of India for kitchen ventilation norms
-
Some apartments require society or builder approval for ducting through outer walls
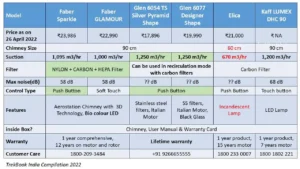
Selection of Chimney Chimney
Here are key guidelines to design and install an effective kitchen chimney in Indian homes:
Match Hood Width to Stove Size
-
-
Your chimney’s capture area should extend beyond the cooktop on both sides.
-
Recommended widths:
| Stove Type | Chimney Width |
|---|---|
| 2‑burner gas or electric | 60 cm hood |
| 3–4‑burner | 90 cm hood |
Optimal Mounting Height
-
-
-
For wall‑mounted chimneys over gas stoves, place the hood 24–30 inches (60–75 cm) above the cooking surface.
-
Example: if your countertop is 34 inches (86 cm) off the floor, mark the hood bottom at roughly 58–64 inches (147–163 cm) from the floor.
-
Too low risks heat damage and head bumps; too high weakens suction.
-
-
Choose a Suitable Wall
-
-
Ideally install on an external wall with a clear path for ducting.
-
Avoid placing the hood under a window (drafts reduce effectiveness) or behind cabinets that block access and inspection.
-
Duct Design & Sizing
-
Pipe diameter: at least 6 inches (150 mm).
-
Length: keep the duct run as short as possible, ideally 6–8 feet (2–2.5 m). Runs over 10 feet (3 m) can degrade performance ContractorBhai.
-
Bends: limit to 2–3 × 90° elbows (or equivalent 45° bends) to minimize pressure loss and noise. ContractorBhai
-
Use rigid stainless‑steel, aluminum, or PVC ducting rather than flexible plastic to avoid cracking and blockages. Price India
Airflow Capacity (Suction Power)
-
-
Chimneys are rated in m³/hr. For typical Indian kitchens, aim for:
-
400–600 m³/hr for light to moderate cooking
-
600–1,000 m³/hr (or higher) if you fry often or have a large open‐plan kitchen
-
-
Filters & Maintenance
-
-
Baffle filters trap grease effectively and are easy to clean.
-
Mesh filters are cheaper but require frequent washing.
-
Plan for monthly cleaning of filters and an accessible oil‑collector tray.
-
Electrical & Safety Considerations
-
-
Provide a dedicated 10 A–15 A socket 6–12 inches above the hood—ideally to one side for easy access.
-
Conceal wiring within a conduit or behind cabinetry.
-
Ensure the motor and ductwork are earthed and grounded per local electrical codes. Price India
-
Termination & Back‑Draft Prevention
-
-
At the exterior wall, fit an anti‑backdraft damper to stop outside air (and insects) from entering when the chimney is off.
-
Seal around the duct penetration to prevent water ingress and heat loss.
-
Best kitchen chimney selection parameters in India
Why Filterless Auto‑Clean Chimneys Are Best for Low Maintenance
-
Auto‑clean technology uses heat/centrifugal action to remove grease into a collector tray—no manual filter washing. The Economic Times+11mint+11The Economic Times+11
-
Filterless design eliminates mesh filters entirely, significantly reducing the need to dismantle and scrub clogged filters. mint+1
-
Hands-free features like gesture controls and touch interfaces cut down the physical operation burden. mint
-
Suction around 1200 m³/hr handles oily Indian cooking efficiently—less residue buildup, fewer issues long-term.
-
.
Tips for Lowest Maintenance Use
-
Choose right width: 60 cm for 2–3 burner hob, 90 cm for larger cooktops.
-
Ensure proper installation: minimal bends in duct, right height (~65–75 cm above gas stove).
-
Empty the oil tray monthly—a quick and easy task.
-
Avoid touch panel issues: some Reddit users noted logic board repairs can be costly—stick with reliable brands. Reddit
-
Check local service reputation for your city—brands like Elica and Faber have generally strong customer support. mint+7Reddit+7Reddit+7
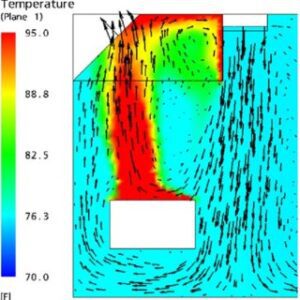
CFD-based Airflow Analysis for Chimney
CFD-based airflow analysis recommendation tailored for kitchen chimneys in Indian homes. This type of analysis helps optimize smoke extraction, air quality, and thermal comfort—especially important in homes with frequent high-temperature cooking like tadka or frying.
Objectives of CFD Analysis for Kitchen Chimney
-
Evaluate smoke and hot air flow paths
-
Optimize chimney suction position and duct design
-
Ensure proper fresh air inflow and thermal comfort
-
Minimize recirculation zones and turbulence near the cooktop
Key Inputs for CFD Modeling
1. Geometry Setup
-
Model the kitchen space, chimney hood, cooking stove, ducting, and external exhaust outlet.
-
Include windows, doors, exhaust fans, or ventilators if present.
2. Boundary Conditions
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Stove heat source | ~2–5 kW (based on number of burners) |
| Cooking emissions | Smoke + moisture at ~150–200°C |
| Chimney inlet velocity | Derived from suction power (e.g. 1000 m³/h) |
| Ambient air | 25–35°C at 1 atm |
| Inlet/outlet vents | Define natural or forced ventilation |
3. Turbulence Model
-
Use k–ε (standard or RNG) or k–ω SST models—good for indoor airflow and buoyant plumes.
Parameters to Analyze
-
Velocity streamlines – visualize airflow patterns and suction effectiveness.
-
Smoke (contaminant) dispersion – ensure efficient capture by the hood.
-
Temperature contours – track heat spread and removal rate.
-
Pressure drop across the duct – to assess fan load.
-
Recirculation zones – especially around the cooktop or above cabinets.
Software Recommendations
-
ANSYS Fluent or OpenFOAM – detailed 3D simulations
-
SimScale – cloud-based option, easier for collaborative projects
-
COMSOL Multiphysics – for thermal + air quality simulations
Design Optimization Tips Using CFD
-
Check chimney hood position: Ensure full coverage of hot air plume.
-
Modify duct bends: Reduce bends or add smooth curvature to reduce losses.
-
Balance inflow/outflow: Add makeup air inlets to avoid negative pressure zones.
-
Simulate during multiple cooking events: Understand behavior with 2 or more burners running.
Deliverables from CFD Report
-
3D renderings of airflow and temperature
-
Capture efficiency of chimney
-
Flow velocity vectors and streamlines
-
Recommendations on chimney height, duct diameter, fan specs
Reference
- The hindu article –Best Kitchen Chimney Selection Guide in India
- Tech Home Blog, Best Kitchen Chimney 2023 Buyers Guide