Table of Contents
ToggleDesign of jaggery making plant
- Designing a jaggery making plant involves a detailed understanding of the process of converting sugarcane juice into jaggery, including extraction, clarification, boiling, molding, and packaging
- Here’s a breakdown of a typical jaggery making plant design suitable for small to medium-scale production (1–5 tons per day), including layout, equipment, and technical considerations
Process Flow for Jaggery Production
-
Sugarcane Feeding & Washing
-
Juice Extraction (Crusher/Mill)
-
Juice Filtration/Clarification
-
Boiling & Concentration (Furnace + Pan)
-
Molding/Cooling
-
Packaging & Storage
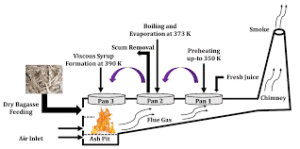
Plant Layout Design
A. Area Requirements (for ~2 TPD capacity):
-
Total: ~3000–5000 sq ft
-
Segmented into:
-
Sugarcane storage and feeding area
-
Crushing & juice collection
-
Boiling/furnace area (chimney + pan)
-
Cooling & molding platform
-
Storage & packing area
-
Fuel storage (biomass or bagasse)
-
Wastewater drainage system
-
Equipment and Machinery
| Section | Equipment | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding | Conveyor or manual feeding | Optional automation |
| Extraction | 3-roller mill / crusher | Powered by motor or engine |
| Clarification | Juice tank, lime dosing | Settling tank for impurities |
| Boiling | Mild steel or SS pan (3-part or 4-part) | Direct heating by biomass, bagasse, or gas |
| Furnace | Brick or metal biomass furnace | With flue gas chimney |
| Cooling | Wooden/mild steel trays | Manual or semi-mechanized |
| Packaging | Molds, scales, wrapping | Manual or auto-packing |

Furnace Design
A good boiling furnace is key for fuel efficiency and smokeless operation.
Options:
-
Traditional chula (high fuel use, more pollution)
-
Improved biomass furnace (20–30% more efficient)
-
Bagasse-based system (saves cost if bagasse is used)
-
CFD-designed furnace (optional for high-end efficiency)
Fuel used: Bagasse, wood, or biomass briquettes.
Chimney and Ventilation
-
Chimney height: 25–30 ft (above roof level)
-
Diameter: 9–12 inches (for natural draft)
-
Should have:
-
Spark arrestor
-
Rain cap
-
Baffle plate (optional)
-
Design of Jaggery Furnace Using Biomass Pellets
The jaggery furnace is a crucial component in jaggery production, traditionally fueled by bagasse (sugarcane residue) or firewood. However, the adoption of biomass pellets as a fuel source enhances efficiency, sustainability, and reduces environmental impact.

1. Advantages of Using Biomass Pellets in Jaggery Furnace
- Higher Efficiency: Biomass pellets have a higher calorific value (3500-4500 kcal/kg) than bagasse, resulting in better combustion.
- Low Emissions: Produces less smoke, ash, and particulate matter, improving working conditions.
- Consistent Heat Supply: Uniform pellet size allows controlled combustion and steady heating, leading to better jaggery quality.
- Reduced Waste: Unlike bagasse, which contains moisture, pellets are dry and have higher energy conversion efficiency.
- Sustainability: Pellets are made from agricultural residues, sawdust, and other biomass waste, making them eco-friendly.

2. Design Features of a Biomass Pellet-Fired Jaggery Furnace
a) Furnace Structure
- Material: Built using fire-resistant bricks with insulation for heat retention.
- Dimensions: Designed based on capacity requirements, with a firebox to accommodate pellet-based combustion.
b) Combustion Chamber
- Equipped with a grate system for pellet feeding and controlled burning.
- Uses an air supply system (forced draft fans or blowers) to enhance combustion efficiency.
c) Fuel Feeding Mechanism
- Manual Feeding: Small-scale furnaces may use manual feeding of pellets.
- Automated Feeding: Larger units can have an automatic pellet feeder with a hopper, ensuring a continuous and controlled fuel supply.
d) Heat Transfer System
- Boiling Pans: Iron or stainless steel pans placed strategically over the fire chamber to ensure even heat distribution.
- Flue Gas Pathways: Designed to maximize heat utilization before gases exit through the chimney.
e) Chimney and Emission Control
- High-efficiency chimney for proper smoke exhaust.
- Cyclone dust collectors or wet scrubbers can be added to reduce particulate emissions.

3. Working Mechanism of Biomass Pellet Jaggery Furnace
- Pellet Feeding: Biomass pellets are fed into the combustion chamber either manually or automatically.
- Combustion Process: Air is supplied to ensure complete combustion, generating high heat.
- Heat Transfer: The heat is transferred to the boiling pans, where sugarcane juice is concentrated into jaggery.
- Exhaust & Heat Recovery: Waste heat is used to preheat air or juice, increasing overall efficiency.
- Jaggery Collection: Once the juice reaches the desired consistency, it is cooled and molded into jaggery blocks.
4. Efficiency and Performance Comparison
| Parameter | Traditional Bagasse Furnace | Biomass Pellet Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Efficiency | ~20-30% | ~40-50% |
| Emissions | High smoke & CO₂ | Low smoke, eco-friendly |
| Heat Control | Inconsistent | Uniform, controlled |
| Maintenance | Frequent ash removal | Minimal ash formation |
| Fuel Availability | Seasonal (bagasse-dependent) | Year-round (pellets) |
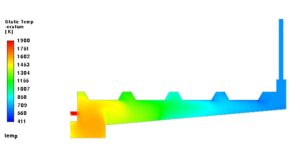
CFD Modeling for Design of Jaggery Furnace
- CFD Modeling for Design of Jaggery Furnace is an innovative and valuable approach to improve energy efficiency, optimize combustion, and reduce emissions during jaggery (gur) production.
- This process traditionally uses biomass or bagasse as fuel in rural setups, often with inefficient furnace designs.
Why Use CFD in Jaggery Furnace Design?
-
Optimize Furnace Geometry:
-
Analyze how furnace shape affects heat transfer.
-
Improve air-fuel mixing for better combustion.
-
-
Improve Thermal Efficiency:
-
Reduce fuel consumption by identifying heat losses.
-
Ensure uniform heat distribution for better sugarcane juice concentration.
-
-
Reduce Emissions:
-
Model flue gas composition and reduce CO, NOx, and unburned hydrocarbons.
-
-
Enhance Safety:
-
Analyze hotspots and prevent overheating.
-
-
Economic Benefits:
-
Lower operating costs by reducing fuel and enhancing output.
-
Key Aspects Modeled in CFD:
-
Combustion Modeling:
-
Biomass/bagasse combustion with proper air supply.
-
Models: Eddy Dissipation, Finite Rate, or Non-premixed combustion.
-
-
Heat Transfer:
-
Conduction through furnace walls.
-
Convection in flue gas flow.
-
Radiation modeling from flame and hot surfaces.
-
-
Fluid Flow:
-
Air and flue gas velocity distribution.
-
Draft behavior and chimney effect.
-
-
Pollutant Emission:
-
Soot, CO₂, CO, and NOₓ estimation.
-
-
Evaporation:
-
Simulation of juice concentration using energy balance.
-
Advantages Over Traditional Design:
| Traditional Approach | CFD-Based Approach |
|---|---|
| Trial-and-error design | Simulation-guided precision |
| High fuel use | Optimized combustion |
| Uneven heating | Uniform heat distribution |
| No emissions control | Emission analysis & reduction |
Conclusion
- A jaggery furnace using biomass pellets offers higher efficiency, cleaner combustion, and sustainable fuel utilization compared to traditional furnaces. Implementing automated feeding and air control systems further enhances productivity, making it a viable alternative for modern jaggery production.
- Would you like a 3D model or schematic diagram of the furnace design?
- CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) allows for virtual testing and optimization of these designs
