Steps in Making Organic Jaggery
- Making organic jaggery at home involves using organically grown sugarcane and ensuring that the process is free from any chemical additives or preservatives.
- Here’s a step-by-step guide for making organic jaggery:
Ingredients and Equipment
- Organic Sugarcane: Ensure the sugarcane is organically grown, free from pesticides and chemicals.
- Large Pot or Kettle: For boiling the sugarcane juice.
- Strainer or Muslin Cloth: To filter the juice.
- Wooden or Metal Stirrer: For stirring the juice.
- Lime or Ladyfinger Plant: Organic options for clarifying the juice (optional).
- Molds: To shape the jaggery (optional).

Preparation of Organic Sugarcane
- Select Fresh Organic Sugarcane: Choose sugarcane that is fresh, firm, and organically grown.
- Clean the Sugarcane: Wash the sugarcane thoroughly to remove any dirt or impurities.
- Peel the Sugarcane: Use a knife to peel off the outer layer, revealing the juicy inner part.
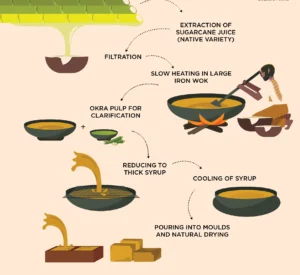
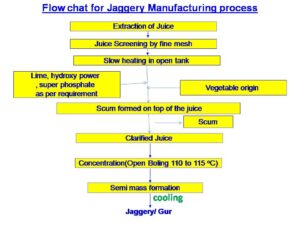
Juice Extraction
- Extract the Juice: Use a sugarcane juicer or press to extract the juice. Collect the juice in a clean container.
- Filter the Juice: Use a strainer or muslin cloth to remove any solids or fibers from the juice.

Clarification (Optional)
- Organic Clarification:
- If the juice is cloudy, you can clarify it using organic methods. Add a small amount of lime or ladyfinger (okra) extract to the boiling juice to help settle impurities. The juice can then be filtered again if needed.
Boiling the Juice
- Boil the Juice: Pour the filtered juice into a large pot or kettle and begin heating it over a medium flame.
- Stir Constantly: Stir the juice continuously to prevent it from sticking or burning. As it boils, impurities will rise to the surface, which should be skimmed off regularly.
- Reduction: Boil the juice until it thickens and reaches a syrup-like consistency. This process can take several hours.
- Test for Readiness: Drop a small amount of the syrup into cold water; if it forms a soft ball, it’s ready to be molded.
Forming the Organic Jaggery
- Pour into Molds: Pour the thick syrup into molds or onto a greased surface. Let it cool down and solidify.
- Cooling and Solidifying: Allow the syrup to cool at room temperature until it hardens into jaggery blocks or powder.
Storage
- Store Properly: Once the jaggery has solidified, store it in an airtight container to maintain its freshness and prevent moisture from affecting it.
Tips for Organic Jaggery:
- Patience is Key: Organic jaggery making, like traditional methods, requires patience and careful attention during boiling.
- Natural Sweetness: Organic jaggery retains a higher nutrient content and a richer, more complex flavor compared to commercial options.
- Avoid Additives: Ensure that no chemicals or artificial additives are used at any stage of the process.
Organic jaggery made at home is a pure, unrefined sweetener that offers a healthier alternative to processed sugars.
How to make organic jaggery powder
- Making organic jaggery powder at home involves a similar process to making traditional jaggery, with an additional step to granulate the solid jaggery into powder form.
- Here’s how you can do it:
1. Ingredients and Equipment
- Organic Sugarcane: Ensure the sugarcane is organically grown.
- Large Pot or Kettle: For boiling the sugarcane juice.
- Strainer or Muslin Cloth: To filter the juice.
- Wooden or Metal Stirrer: For stirring the juice.
- Blender or Food Processor: For grinding the jaggery into powder.
- Lime or Ladyfinger Plant: Organic options for clarifying the juice (optional).
Preparation of Organic Sugarcane
- Select Fresh Organic Sugarcane: Choose sugarcane that is firm and organically grown.
- Clean the Sugarcane: Wash the sugarcane thoroughly to remove any dirt.
- Peel the Sugarcane: Peel the outer layer of the sugarcane to access the juicy inner part.
Juice Extraction
- Extract the Juice: Use a sugarcane juicer or press to extract the juice. Collect it in a clean container.
- Filter the Juice: Use a strainer or muslin cloth to filter out any solid particles from the juice.
Clarification (Optional)
- Organic Clarification:
- To clarify the juice, you can add a small amount of lime or ladyfinger (okra) extract during boiling. This helps remove impurities naturally. Filter the juice again if necessary.
Boiling the Juice
- Boil the Juice: Pour the filtered juice into a large pot or kettle and begin boiling over medium heat.
- Stir Regularly: Stir the juice continuously to prevent it from burning. As it boils, skim off any scum that forms on the surface.
- Reduce the Juice: Continue boiling until the juice thickens into a syrupy consistency. This can take several hours.
- Test for Readiness: Drop a small amount of syrup into cold water; if it forms a soft ball, it’s ready for the next step.
Cooling and Granulating
- Allow to Cool Slightly: Once the syrup is ready, allow it to cool slightly but not fully harden.
- Granulate the Syrup: Before the syrup fully solidifies, stir it continuously in the pot. This will cause the syrup to break up into granules instead of forming a solid block.
- Spread Out to Cool: Spread the granulated syrup on a flat surface and allow it to cool completely.
Grinding into Powder
- Blend the Granules: Once the granules are fully cooled, place them in a blender or food processor. Pulse until the jaggery reaches a fine powder consistency.
- Sift the Powder: To ensure uniformity, you can sift the powder through a fine mesh strainer.

Storage
- Store in an Airtight Container: Place the jaggery powder in an airtight container to keep it dry and fresh.

Tips for Organic Jaggery Powder:
- Avoid Moisture: Ensure that the jaggery powder is stored in a dry place to prevent clumping.
- Use as a Sweetener: Organic jaggery powder can be used as a natural sweetener in tea, coffee, desserts, and other recipes.
What chemical are used in Adulteration of Jaggery
Conclusion
- Organic jaggery powder is a versatile and healthy alternative to refined sugar, retaining the nutrients and rich flavor of traditional jaggery while being more convenient to use in powdered form
- Choosing organic or traditionally made jaggery helps avoid these harmful adulterants and ensures a healthier, more nutritious product.


