Mechanicsm of Inverter AC
- An inverter-type air conditioner is a type of air conditioner that uses an inverter to control the speed of the compressor motor. In traditional air conditioners, the compressor is either on or off, and it operates at a fixed speed. In contrast, inverter-type ACs have a variable frequency drive that allows the compressor to operate at different speeds depending on the cooling demand
- When the cooling demand is low, the compressor operates at a low speed, consuming less energy. As the cooling demand increases, the compressor speed increases to provide more cooling. This results in more energy-efficient and precise temperature control compared to traditional air conditioners.

- Inverter-type ACs also have other features that contribute to their energy efficiencies, such as DC motors that consume less power, improved heat exchangers, and optimized airflows. Inverter-type ACs are generally more expensive than traditional air conditioners, but their energy efficiency and other benefits can result in lower long-term operating costs.
- Inverter ACs use a variable frequency drive that adjusts the compressor speed according to the temperature in the room, resulting in lower energy consumption. This also leads to more precise temperature control, which can further reduce energy consumption. In addition, many inverter ACs have features like improved heat exchangers and optimized airflows, which can further improve their energy efficiency.
The energy efficiency of an inverter AC is typically measured by its Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) rating. The SEER rating is a measure of the AC’s cooling output over a season, divided by the amount of energy it consumes over that same season. The higher the SEER rating, the more energy-efficient the AC.
Overall, inverter ACs are generally more energy-efficient than traditional non-inverter ACs, which can result in lower energy bills and reduced environmental impact.
Difference Between Traditional and Inverter AC
- The main difference between traditional and inverter ACs lies in the way they control the speed of the compressor motor
- Traditional ACs have a fixed-speed compressor that operates at a fixed rate, typically turning on and off to maintain the desired temperature in the room. This can result in higher energy consumption and less precise temperature control.
- Inverter ACs, on the other hand, have a variable speed compressor that can adjust its speed to match the cooling demand. The compressor speed is controlled by an inverter, which adjusts the frequency of the electrical current to the compressor motor.
- This allows the compressor to operate at different speeds, depending on the cooling demand, resulting in more precise temperature control and lower energy consumption
- Other differences between traditional and inverter ACs include:
- Noise level: Inverter ACs are typically quieter than traditional ACs, as they do not have the same abrupt start and stop of the compressor.
- Cooling speed: Inverter ACs can cool a room faster than traditional ACs, as they can operate at a higher speed during the initial cooling period.
- Cost: Inverter ACs are generally more expensive than traditional ACs, but they can provide long-term savings through their energy efficiency.
- Lifespan: Inverter ACs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional ACs, as they operate more smoothly and have fewer mechanical parts that can wear out.
Overall, inverter ACs offer more precise temperature control, lower energy consumption, quieter operation, faster cooling, and longer lifespan compared to traditional ACs.
Benefits of Non-Inverter air conditioners (NIAC)
Inverter-type air conditioners have several benefits over traditional non-inverter air conditioners, including:
Energy efficiency:
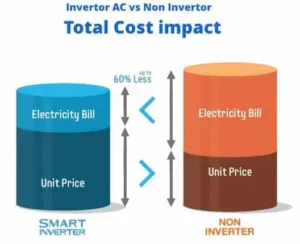
- Inverter-type ACs are more energy-efficient compared to non-inverter ACs as they can adjust the compressor speed according to the cooling demand. This results in a reduction of electricity consumption and lower electricity bills.
- Inverter ACs are generally more energy-efficient compared to traditional non-inverter ACs. This is because inverter ACs can adjust the compressor speed to match the cooling demand, resulting in lower energy consumption. Traditional ACs have a fixed-speed compressor that turns on and off depending on the temperature in the room, leading to higher energy consumption
Quieter operation:
- Inverter ACs operate at a much lower noise level compared to non-inverter ACs due to the constant and smooth operation of the compressor.
Faster cooling:
- Inverter ACs can cool a room faster compared to non-inverter ACs, as the compressor runs at a higher speed during the initial cooling period.

Better temperature control:
- Inverter ACs offer more precise temperature control than non-inverter ACs, as the compressor speed can be adjusted according to the required temperature.
Longer lifespan:
- Inverter ACs have a longer lifespan compared to non-inverter ACs as the compressor operates smoothly and consistently, reducing wear and tear.

Overall, inverter-type air conditioners provide better energy efficiency, quieter operation, faster cooling, better temperature control, and longer lifespan compared to non-inverter air conditioners.