Heating and Ventilations Analysis Tools
For analyzing heating and ventilation systems specifically, here are some robust software options:
1. EnergyPlusMenus
- Strengths: Analyzes complex heating, cooling, ventilation, and lighting systems, modeling energy use and thermal loads in detail.
- Applications: Energy efficiency analysis, HVAC load calculation, and thermal comfort evaluation.
2. COMSOL Multiphysics
- Strengths: Supports heat transfer and fluid dynamics modules, allowing detailed simulations of heating and ventilation, including CFD.
- Applications: Thermal management, airflow analysis, HVAC component testing, and ventilation effectiveness studies.
3. ANSYS Fluent
- Strengths: Provides advanced Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) capabilities, ideal for airflow and ventilation analysis in complex environments.
- Applications: Ventilation design, air distribution, thermal management, and pollutant dispersion modeling.

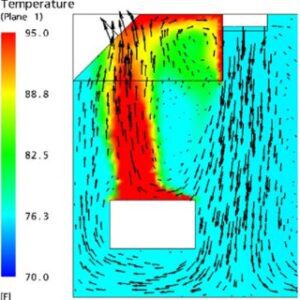
CFD of kitchen chimney
4. Trane TRACE 3D Plus
- Strengths: Specialized for HVAC load analysis and system design, focusing on energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Applications: Load calculations, HVAC system design, and energy consumption analysis.
5. OpenFOAM
- Strengths: Open-source CFD platform suitable for advanced airflow and thermal analysis, particularly useful for customization in HVAC research.
- Applications: Ventilation performance, heat transfer in ducts, and indoor air quality studies.
6. IDA ICE (Indoor Climate and Energy)
- Strengths: Detailed simulation of building systems and indoor environments, accounting for thermal comfort and air quality.
- Applications: Indoor climate control, HVAC performance, and air quality assessment.
- These tools help analyze everything from simple HVAC loads to complex airflow dynamics and pollutant modeling, making them valuable for optimizing heating and ventilation system performance.