Benefits of GPU cards
- GPU cards, or Graphics Processing Units, offer several benefits across various applications and industries due to their specialized architecture optimized for parallel processing of graphics and other computational tasks.
- Here are some of the key benefits of GPU cards
- Graphics Rendering:
- GPUs excel at rendering high-quality graphics and visual effects in video games, movies, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) applications.
- Their parallel processing capabilities enable real-time rendering of complex scenes with detailed textures, lighting effects, and simulations.

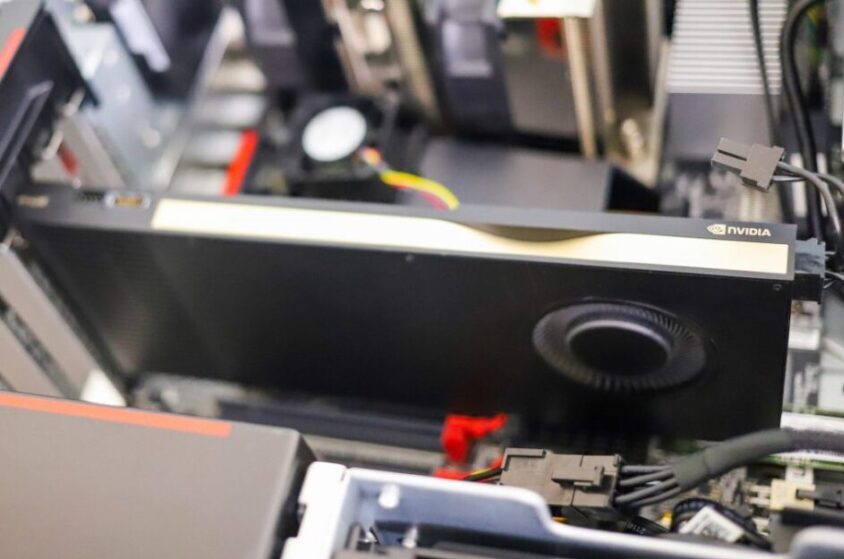
GPU cards for P720 Lenovo workstation
- Compute Acceleration:
- GPUs are highly efficient at parallel computing tasks, making them well-suited for accelerating compute-intensive workloads in fields such as scientific research, data analysis, machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI). Tasks like matrix multiplication, neural network training, and image processing can benefit significantly from GPU acceleration.
- Parallel Processing Power:
- GPUs contain thousands of processing cores that can perform computations simultaneously, enabling massive parallelism and faster execution of tasks compared to traditional CPUs. This parallel processing power allows GPUs to handle large datasets and complex algorithms more efficiently.
- CUDA and OpenCL Support:
- Many GPUs support programming frameworks such as CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) for NVIDIA GPUs and OpenCL (Open Computing Language) for both NVIDIA and AMD GPUs. These frameworks provide developers with tools and libraries for writing parallel code and harnessing the full potential of GPU computing.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks:
- GPUs have become essential for training and deploying deep learning models and neural networks due to their ability to process large volumes of data in parallel. Deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and MXNet leverage GPU acceleration to accelerate model training and inference tasks.
- Energy Efficiency:
- GPUs offer high performance with relatively low power consumption compared to CPUs for certain types of computations. This energy efficiency is particularly advantageous in data centers and large-scale computing environments where power consumption and cooling costs are significant factors.
- Real-Time Graphics and Interactivity:
- In gaming and interactive applications, GPUs enable real-time rendering of immersive 3D environments, fluid animation, and responsive user interfaces. The ability to render graphics quickly and interactively enhances the gaming experience and user engagement in virtual environments.
- Specialized Workloads:
- GPUs can be customized and optimized for specific workloads and applications, such as medical imaging, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), financial modeling, and weather forecasting
- Customized GPU architectures and software libraries can improve performance and accuracy in these specialized domains
- GPUs can be customized and optimized for specific workloads and applications, such as medical imaging, computational fluid dynamics (CFD), financial modeling, and weather forecasting. Customized GPU architectures and software libraries can improve performance and accuracy in these specialized domains

How to select Graphics cards
Purpose and Usage:
-
- Determine the primary purpose of the graphics card.
- Are you using it for gaming, content creation, video editing, 3D modeling, or other professional applications?
- Different tasks may require different levels of performance and features.
Budget:
- Establish a budget for your graphics card purchase.
- Graphics cards come in various price ranges, so determining how much you’re willing to spend can help narrow down your options.
Performance Requirements:
- Consider the performance requirements of your intended use.
- For gaming, factors such as resolution (1080p, 1440p, 4K) and desired frame rates influence the choice of GPU. For professional applications, consider factors like rendering times, viewport performance, and software compatibility.
Compatibility:
- Check the compatibility of the graphics card with your system, including the motherboard, power supply unit (PSU),
- Physical dimensions of the case.
- Ensure that your PSU can supply enough power and that the card fits within your case.
Memory (VRAM):
-
- Consider the amount of video memory (VRAM) the graphics card offers. Higher VRAM capacities are beneficial for handling larger textures, higher resolutions, and more complex scenes in games and professional applications.
Connectivity:
-
- Check the video output connectors on the graphics card to ensure compatibility with your monitor(s) and other display devices. Common connectors include HDMI, DisplayPort, and DVI.
- Brand and Model:
- Research different graphics card brands and models to find one that offers the best combination of performance, features, reliability, and customer support. NVIDIA and AMD are the two main GPU manufacturers, with various board partners producing cards based on their designs.
Reviews and Benchmarks:
-
- Read reviews and benchmarks from reputable sources to get an understanding of the graphics card’s real-world performance and reliability. Look for reviews that focus on your intended use case (e.g., gaming benchmarks for gaming GPUs).
Future Upgradability:
-
- Consider whether you plan to upgrade your graphics card in the future.
- Choosing a graphics card with a good balance of performance and price can ensure it remains relevant for a longer period before needing an upgrade.
Warranty and Support:
- Check the warranty coverage and customer support offered by the manufacturer. A longer warranty period and reliable customer support can provide peace of mind and assistance in case of issues.
Best GPU Cards on Gaming or CAD Software
- The best GPU cards on the market often depend on factors such as budget, intended use (gaming, professional workloads like rendering or machine learning), and availability.
- Here are some GPUs that were highly regarded at that time across different price ranges and purposes:
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090:
- Positioned as a flagship GPU, the RTX 3090 offers unparalleled performance suitable for 4K gaming, high-resolution content creation, and demanding professional workloads like 3D rendering and AI development.
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080:
- The RTX 3080 provides excellent performance for 4K gaming and high-refresh-rate gaming at 1440p. It’s also suitable for content creators who work with high-resolution video editing and 3D rendering.
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3070:
- The RTX 3070 offers great performance for high-quality gaming at 1440p and solid performance at 4K.
- It’s a more affordable option compared to the RTX 3080 and RTX 3090 while still delivering excellent value.
- AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT:
- AMD’s flagship GPU, the RX 6900 XT, competes with NVIDIA’s high-end offerings.
- It’s suitable for high-resolution gaming, content creation, and professional workloads.
- AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT:
- The RX 6800 XT offers strong performance for gaming at 1440p and 4K resolutions.
- It’s also a competitive option for content creators and professionals who need GPU acceleration.

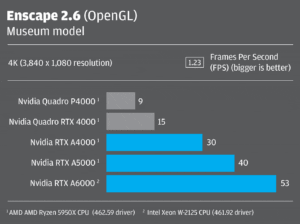
Comparison of NVIDIA Graphics cards
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 Ti:
- The RTX 3060 Ti provides excellent value for gaming at 1080p and 1440p resolutions.
- It’s also suitable for entry-level content creation tasks and offers ray-tracing capabilities.
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3050 Ti / RTX 3050:
- These GPUs are aimed at budget-conscious gamers and offer good performance for 1080p gaming and entry-level content creation.
- It’s important to note that GPU availability and pricing can fluctuate due to factors like cryptocurrency mining demand, manufacturing constraints, and global supply chain issues.
- Additionally, newer GPU models may have been released since my last update, so I recommend checking recent reviews and benchmarks for the latest information on GPU performance and availability.
- There is a list of some NVIDIA graphics cards from different series.
- Note that newer models may have been released since then, and you should check the official NVIDIA website or retailers for the latest information:
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX Series:
- GeForce RTX 3090
- GeForce RTX 3080
- GeForce RTX 3070
- GeForce RTX 3060 Ti
- GeForce RTX 3060
- NVIDIA GeForce GTX Series:
- GeForce GTX 1660 Ti
- GeForce GTX 1660 Super
- GeForce GTX 1660
- GeForce GTX 1650 Super
- GeForce GTX 1650
- NVIDIA Titan Series:
- NVIDIA Titan RTX
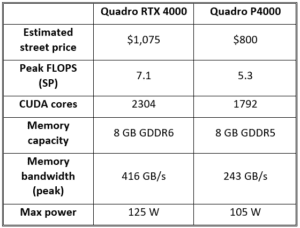
- NVIDIA Quadro Series (Professional GPUs):
- Quadro RTX 8000
- Quadro RTX 6000
- Quadro RTX 5000
- Quadro P5000
- Quadro P4000
- Quadro P2000
- Quadro GV100
- Quadro M6000
- Quadro M5000
- NVIDIA A series (Professional GPUs):
- NVIDIA A6000
- NVIDIA A5000
- NVIDIA A4000
- Graphics cards, while integral components in modern computing, can encounter several issues, both hardware and software-related.
- Here are some common problems associated with graphics cards:
Driver Issues:
- Graphics cards require specific drivers to function properly. Outdated, incompatible, or corrupted drivers can cause various problems such as graphical glitches, crashes, or performance issues
Overheating:
- Graphics cards generate a significant amount of heat during operation.
- If the cooling system is inadequate or clogged with dust, the card can overheat, leading to performance degradation, system instability, or even hardware damage.
Artifacting:
- Artifacting refers to visual anomalies such as flickering, distortion, or random colored pixels appearing on the screen. This can be caused by overheating, defective hardware, or overclocking.
Screen Tearing:
- Screen tearing occurs when the monitor’s refresh rate and the graphics card’s frame rate are out of sync.
- This results in a torn appearance on the screen, where different parts of the image seem to be from different frames.
Driver Crashes:
- Incompatibility issues, software conflicts, or hardware problems can cause graphics card drivers to crash.
- This can result in system instability, freezes, or even blue screen errors (BSOD).
Power Supply Problems
- Graphics cards require sufficient power to operate correctly.
- If the power supply unit (PSU) is inadequate or failing, it can cause the graphics card to malfunction or fail altogether.
Physical Damage:
- Accidental physical damage to the graphics card, such as bending, broken connectors, or damaged circuits, can render the card inoperable or cause performance issues.
Memory Errors:
- Errors in the VRAM (Video RAM) or onboard memory of the graphics card can lead to graphical artifacts, crashes, or system instability.
Compatibility Issues:
- Not all graphics cards are compatible with every motherboard or system configuration.
- Compatibility issues can arise due to differences in interface standards (PCIe, AGP, etc.), power requirements, or driver support.
Manufacturing Defects:
- Like any electronic component, graphics cards can suffer from manufacturing defects that may not become apparent until the card is in use. Common defects include soldering issues, faulty components, or poor quality control during assembly.
- Addressing graphics card issues often involves troubleshooting steps such as updating drivers, cleaning the card and its cooling system, checking hardware connections, monitoring temperatures, and possibly replacing or repairing the card if necessary.

How to resolve issues in GPU cards
- Resolving issues with GPU cards involves a systematic approach to identify and address the specific problem.
- GPU RTX A4000 cards Thinkstation Lenovo Workstation
- To find specific information about the Lenovo ThinkStation A4000 and its GPU, I recommend checking the official Lenovo website, and product documentation, or contacting Lenovo’s customer support for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
- Additionally, user reviews and discussions on forums can provide insights into the real-world performance of the system and its components
- Here are general steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve GPU-related issues:
Update Drivers:
- Ensure that you have the latest graphics drivers installed for your GPU.
- Visit the official website of the GPU manufacturer (NVIDIA, AMD, or Intel) to download and install the most recent drivers.
Check for Overheating:
-
- Monitor the GPU temperature using software tools like MSI Afterburner or HWMonitor. Ensure that the cooling system is functioning correctly, and clean any dust or debris from the fans and heat sinks. Consider improving case ventilation if necessary.
Inspect Physical Connections:
-
- Make sure the GPU is properly seated in the PCIe slot on the motherboard. Check power connectors and ensure they are securely connected. If your GPU requires additional power, ensure that the power supply is sufficient and cables are connected correctly.
- Verify Power Supply:
- Ensure that your power supply unit (PSU) provides sufficient power for your GPU. Check if the PSU meets the recommended power requirements of the GPU. Consider upgrading the PSU if needed.
- Test with Different PCIe Slot:
- If you have multiple PCIe slots on your motherboard, try installing the GPU in a different slot to rule out any issues with the specific slot.
- Check for Physical Damage:
- Inspect the GPU for any signs of physical damage, such as bent pins, damaged connectors, or burnt components. If you find any issues, it might be necessary to seek professional assistance or replace the GPU.
- Disable Overclocking:
- If you have overclocked your GPU, revert it to the default clock settings. Overclocking can lead to instability and overheating. Test the GPU’s performance without overclocking to see if the issue persists.
- Run Diagnostic Tools:
- Use diagnostic tools like GPU-Z or FurMark to test the GPU’s stability and performance.
- These tools can help identify issues with the GPU’s hardware components.
- Check for Software Conflicts:
- Investigate if there are conflicts between the GPU drivers and other software on your system.
- Disable unnecessary background applications and antivirus software temporarily to see if the issue persists.
- Test in Another System:
- If possible, test the GPU in another computer to determine whether the issue is related to the GPU or the system.
- If the problem persists in a different system, it’s likely a GPU hardware issue.
- Contact Manufacturer Support:
- If you’ve tried all the troubleshooting steps and the issue persists, consider reaching out to the manufacturer’s customer support for further assistance.
- They may provide additional guidance or offer a warranty replacement if applicable.
Conclusion
- Remember to document any error messages, symptoms, or changes you observe during the troubleshooting process.
- This information can be helpful when seeking assistance from forums, support communities, or the GPU manufacturer.
- By considering these factors and doing thorough research, you can select a graphics card that best suits your needs and budget while providing optimal performance and compatibility for your system.